Differences in survival among 13 Listeria monocytogenes strains in a dynamic model of the stomach and small intestine
- PMID: 18586963
- PMCID: PMC2546618
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00319-08
Differences in survival among 13 Listeria monocytogenes strains in a dynamic model of the stomach and small intestine
Abstract
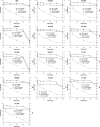
Thirteen Listeria monocytogenes strains were compared for the ability to survive in a dynamic gastrointestinal model. Strains displayed various degrees of susceptibility to gastric acidity; however, strain-to-strain variations became evident mainly after 90 min of exposure (pH 2.0). Cell levels transferred to the intestine depended on initial populations, while reductions during intestinal exposure were relatively small for all strains.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Survival of Listeria monocytogenes in a simulated dynamic gastrointestinal model during storage of inoculated bologna and salami slices in vacuum packages.J Food Prot. 2008 Oct;71(10):2014-23. doi: 10.4315/0362-028x-71.10.2014. J Food Prot. 2008. PMID: 18939746
-
Effect of fat content on survival of Listeria monocytogenes during simulated digestion of inoculated beef frankfurters stored at 7 degrees C.Food Microbiol. 2009 Aug;26(5):483-90. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2009.02.011. Epub 2009 Mar 10. Food Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19465244
-
An agent-based simulator for the gastrointestinal pathway of Listeria monocytogenes.Int J Food Microbiol. 2020 Nov 16;333:108776. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108776. Epub 2020 Jul 10. Int J Food Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32693315
-
Effect of bacteriocin-producing lactobacilli on the survival of Escherichia coli and Listeria in a dynamic model of the stomach and the small intestine.Int J Food Microbiol. 1999 Apr 1;48(1):21-35. doi: 10.1016/s0168-1605(99)00025-2. Int J Food Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10375132
-
Survival of clinical and food isolates of Listeria monocytogenes through simulated gastrointestinal tract conditions.Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2010 Feb;7(2):121-8. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2009.0319. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2010. PMID: 19785538
Cited by
-
Modeling of pathogen survival during simulated gastric digestion.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Feb;77(3):1021-32. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02139-10. Epub 2010 Dec 3. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21131530 Free PMC article.
-
Salt stress phenotypes in Listeria monocytogenes vary by genetic lineage and temperature.Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2010 Dec;7(12):1537-49. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2010.0624. Epub 2010 Aug 14. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2010. PMID: 20707723 Free PMC article.
-
Application of in vitro bioaccessibility and bioavailability methods for calcium, carotenoids, folate, iron, magnesium, polyphenols, zinc, and vitamins B(6), B(12), D, and E.Front Physiol. 2012 Aug 6;3:317. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00317. eCollection 2012. Front Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22934067 Free PMC article.
-
Internalin AB-expressing recombinant Lactobacillus casei protects Caco-2 cells from Listeria monocytogenes-induced damages under simulated intestinal conditions.PLoS One. 2019 Jul 29;14(7):e0220321. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220321. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31356632 Free PMC article.
-
TMT-Based Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Intestinal Organoids Infected by Listeria monocytogenes Strains with Different Virulence.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 2;23(11):6231. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116231. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baranyi, J., and T. A. Roberts. 1994. A dynamic approach to predicting bacterial growth in food. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 23:277-294. - PubMed
-
- Bernbom, N., T. R. Licht, P. Saadbye, F. K. Vogensen, and B. Nørrung. 2006. Lactobacillus plantarum inhibits growth of Listeria monocytogenes in an in vitro continuous flow gut model, but promotes invasion of L. monocytogenes in the gut of gnotobiotic rats. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 108:10-14. - PubMed
-
- Beumer, R. R., J. de Vries, and F. M. Rombouts. 1992. Campylobacter jejuni non-culturable coccoid cells. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 15:153-163. - PubMed
-
- Bishop, D. K., and D. J. Hinrichs. 1987. Adoptive transfer of immunity to Listeria monocytogenes: the influence of in vitro stimulation on lymphocyte subset requirements. J. Immunol. 139:2005-2009. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

