Differences in survival among 13 Listeria monocytogenes strains in a dynamic model of the stomach and small intestine
- PMID: 18586963
- PMCID: PMC2546618
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00319-08
Differences in survival among 13 Listeria monocytogenes strains in a dynamic model of the stomach and small intestine
Abstract
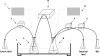
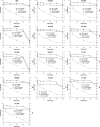
Thirteen Listeria monocytogenes strains were compared for the ability to survive in a dynamic gastrointestinal model. Strains displayed various degrees of susceptibility to gastric acidity; however, strain-to-strain variations became evident mainly after 90 min of exposure (pH 2.0). Cell levels transferred to the intestine depended on initial populations, while reductions during intestinal exposure were relatively small for all strains.
Figures
References
-
- Baranyi, J., and T. A. Roberts. 1994. A dynamic approach to predicting bacterial growth in food. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 23:277-294. - PubMed
-
- Bernbom, N., T. R. Licht, P. Saadbye, F. K. Vogensen, and B. Nørrung. 2006. Lactobacillus plantarum inhibits growth of Listeria monocytogenes in an in vitro continuous flow gut model, but promotes invasion of L. monocytogenes in the gut of gnotobiotic rats. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 108:10-14. - PubMed
-
- Beumer, R. R., J. de Vries, and F. M. Rombouts. 1992. Campylobacter jejuni non-culturable coccoid cells. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 15:153-163. - PubMed
-
- Bishop, D. K., and D. J. Hinrichs. 1987. Adoptive transfer of immunity to Listeria monocytogenes: the influence of in vitro stimulation on lymphocyte subset requirements. J. Immunol. 139:2005-2009. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

