A phosphatidylserine binding site in factor Va C1 domain regulates both assembly and activity of the prothrombinase complex
- PMID: 18587009
- PMCID: PMC2556615
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-02-138941
A phosphatidylserine binding site in factor Va C1 domain regulates both assembly and activity of the prothrombinase complex
Abstract
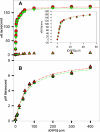
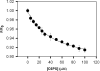
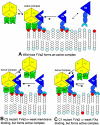
Tightly associated factor V(a) (FVa) and factor X(a) (FXa) serve as the essential prothrombin-activating complex that assembles on phosphatidylserine (PS)-containing platelet membranes during blood coagulation. We have previously shown that (1) a soluble form of PS (C6PS) triggers assembly of a fully active FVa-FXa complex in solution and (2) that 2 molecules of C6PS bind to FVa light chain with one occupying a site in the C2 domain. We expressed human factor V(a) (rFVa) with mutations in either the C1 domain (Y1956,L1957)A, the C2 domain (W2063,W2064)A, or both C domains (Y1956,L1957,W2063,W2064)A. Mutations in the C1 and C1-C2 domains of rFVa reduced the rate of activation of prothrombin to thrombin by FXa in the presence of 400 muM C6PS by 14 000- to 15 000-fold relative to either wild-type or C2 mutant factor rFVa. The K(d')s of FXa binding with rFVa (wild-type, C2 mutant, C1 mutant, and C1-C2 mutant) were 3, 4, 564, and 624 nM, respectively. Equilibrium dialysis experiments detected binding of 4, 3, and 2 molecules of C6PS to wild-type rFVa, C1-mutated, and C1,C2-mutated rFVa, respectively. Because FVa heavy chain binds 2 molecules of C6PS, we conclude that both C2 and C1 domains bind one C6PS, with binding to the C1 domain regulating prothrombinase complex assembly.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The phosphatidylserine binding site of the factor Va C2 domain accounts for membrane binding but does not contribute to the assembly or activity of a human factor Xa-factor Va complex.Biochemistry. 2005 Jan 18;44(2):711-8. doi: 10.1021/bi047962t. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 15641797
-
Mutation of hydrophobic residues in the factor Va C1 and C2 domains blocks membrane-dependent prothrombin activation.J Thromb Haemost. 2005 Feb;3(2):351-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2004.01083.x. J Thromb Haemost. 2005. PMID: 15670043
-
Importance of individual activated protein C cleavage site regions in coagulation factor V for factor Va inactivation and for factor Xa activation.Eur J Biochem. 1999 Feb;260(1):64-75. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00137.x. Eur J Biochem. 1999. PMID: 10091585
-
Factor Va-factor Xa interactions: molecular sites involved in enzyme:cofactor assembly.Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 2002;237:5-11. doi: 10.1080/003655102762377439. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 2002. PMID: 12570161 Review.
-
Blood coagulation factor Va's key interactive residues and regions for prothrombinase assembly and prothrombin binding.J Thromb Haemost. 2019 Aug;17(8):1229-1239. doi: 10.1111/jth.14487. Epub 2019 Jun 17. J Thromb Haemost. 2019. PMID: 31102425 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphatidylserine-induced factor Xa dimerization and binding to factor Va are competing processes in solution.Biochemistry. 2013 Jan 8;52(1):143-51. doi: 10.1021/bi301239z. Epub 2012 Dec 27. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23214401 Free PMC article.
-
Novel role for galectin-8 protein as mediator of coagulation factor V endocytosis by megakaryocytes.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 9;287(11):8327-35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.305151. Epub 2012 Jan 20. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22267735 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the protein C anticoagulant and antiinflammatory pathways.Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(19):2059-69. doi: 10.2174/092986710791233706. Curr Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20423310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Membrane-dependent interaction of factor Xa and prothrombin with factor Va in the prothrombinase complex.Biochemistry. 2009 Jun 9;48(22):5034-41. doi: 10.1021/bi900240g. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19378973 Free PMC article.
-
Factor VIII lacking the C2 domain retains cofactor activity in vitro.J Biol Chem. 2010 Aug 13;285(33):25176-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.106906. Epub 2010 Jun 7. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20529839 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kane WH, Davie EW. Blood coagulation factors V and VIII: structural and functional similarities and their relationship to hemorrhagic and thrombotic disorders. Blood. 1988;71:539–555. - PubMed
-
- Mann KG, Kalafatis M. Factor V: A combination of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde. Blood. 2003;101:20–30. - PubMed
-
- Nesheim ME, Taswell JB, Mann KG. The contribution of bovine Factor V and Factor Va to the activity of prothrombinase. J Biol Chem. 1979;254:10952–10962. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

