Electrostatic readout of DNA microarrays with charged microspheres
- PMID: 18587384
- PMCID: PMC4007654
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt1416
Electrostatic readout of DNA microarrays with charged microspheres
Abstract
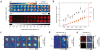
DNA microarrays are used for gene-expression profiling, single-nucleotide polymorphism detection and disease diagnosis. A persistent challenge in this area is the lack of microarray screening technology suitable for integration into routine clinical care. Here, we describe a method for sensitive and label-free electrostatic readout of DNA or RNA hybridization on microarrays. The electrostatic properties of the microarray are measured from the position and motion of charged microspheres randomly dispersed over the surface. We demonstrate nondestructive electrostatic imaging with 10-mum lateral resolution over centimeter-length scales, which is four-orders of magnitude larger than that achievable with conventional scanning electrostatic force microscopy. Changes in surface charge density as a result of specific hybridization can be detected and quantified with 50-pM sensitivity, single base-pair mismatch selectivity and in the presence of complex background. Because the naked eye is sufficient to read out hybridization, this approach may facilitate broad application of multiplexed assays.
Figures



References
-
- Barken K, Haagensen JJ, Tolker-Nielsen T. Advances in nucleic acid-based diagnostics of bacterial infections. Clin Chim Acta. 2007;384:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Abdullah-Sayani A, Bueno-de-Mesquita JM, van de Vijver Marc J. Technology insight: tuning into the genetic orchestra using microarrays—limitations of DNA microarrays in clinical practice. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2006;3:501–516. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

