Therapeutic inhibition of CXCR2 by Reparixin attenuates acute lung injury in mice
- PMID: 18587419
- PMCID: PMC2567887
- DOI: 10.1038/bjp.2008.270
Therapeutic inhibition of CXCR2 by Reparixin attenuates acute lung injury in mice
Abstract
Background and purpose: Acute lung injury (ALI) remains a major challenge in critical care medicine. Both neutrophils and chemokines have been proposed as key components in the development of ALI. The main chemokine receptor on neutrophils is CXCR2, which regulates neutrophil recruitment and vascular permeability, but no small molecule CXCR2 inhibitor has been demonstrated to be effective in ALI or animal models of ALI. To investigate the functional relevance of the CXCR2 inhibitor Reparixin in vivo, we determined its effects in two models of ALI, induced by either lipopolysaccharide (LPS) inhalation or acid instillation.
Experimental approach: In two ALI models in mice, we measured vascular permeability by Evans blue and evaluated neutrophil recruitment into the lung vasculature, interstitium and airspace by flow cytometry.
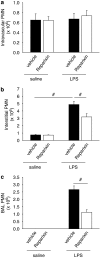
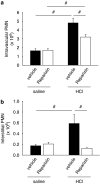
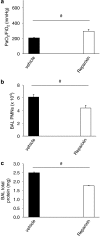
Key results: Pharmacological inhibition of CXCR2 by Reparixin reduced CXCL1-induced leukocyte arrest in the microcirculation of the cremaster muscle, but did not influence arrest in response to leukotriene B4 (LTB4) demonstrating specificity. Reparixin (15 microg g(-1)) reduced neutrophil recruitment in the lung by approximately 50% in a model of LPS-induced ALI. A higher dose did not provide additional reduction of neutrophil recruitment. This dose also reduced accumulation of neutrophils in the interstitial compartment and vascular permeability in LPS-induced ALI. Furthermore, both prophylactic and therapeutic application of Reparixin improved gas exchange, and reduced neutrophil recruitment and vascular permeability in a clinically relevant model of acid-induced ALI.
Conclusions and implications: Reparixin, a non-competitive allosteric CXCR2 inhibitor attenuates ALI by reducing neutrophil recruitment and vascular permeability.
Figures




References
-
- Bokoch GM. Chemoattractant signaling and leukocyte activation. Blood. 1995;86:1649–1660. - PubMed
-
- Camps M, Carozzi A, Schnabel P, Scheer A, Parker PJ, Gierschik P. Isozyme-selective stimulation of phospholipase C-beta 2 by G protein beta gamma-subunits. Nature. 1992;360:684–686. - PubMed
-
- Casilli F, Bianchini A, Gloaguen I, Biordi L, Alesse E, Festuccia C, et al. Inhibition of interleukin-8 (CXCL8/IL-8) responses by repertaxin, a new inhibitor of the chemokine receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2. Biochem Pharmacol. 2005;69:385–394. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

