Anticonvulsant effect of BmK IT2, a sodium channel-specific neurotoxin, in rat models of epilepsy
- PMID: 18587450
- PMCID: PMC2451059
- DOI: 10.1038/bjp.2008.156
Anticonvulsant effect of BmK IT2, a sodium channel-specific neurotoxin, in rat models of epilepsy
Abstract
Background and purpose: The sodium channel is a primary target for treating central nervous system disorders such as epilepsy. In this study the anticonvulsant effect of BmK IT2, a sodium channel-specific neurotoxin, was evaluated in different animal models of epilepsy.
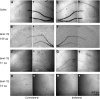
Experimental approach: Experiments were performed on freely moving rats made epileptic by administration of either pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) or pilocarpine. BmK IT2 (0.05-0.5 microg in 2 microl) was microinjected into the CA1 area and its effects on PTZ-induced widespread, seizure-like behaviour and cortex epileptiform EEG, as well as on pilocarpine-induced seizure-like behaviour and c-Fos expression were studied.
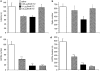
Key results: Intrahippocampal application of BmK IT2 dose-dependently inhibited PTZ-induced seizure-like behaviour, and reduced the numbers and duration of the high amplitude and frequency discharges (HAFDs) of the epileptiform EEG component induced by PTZ. Similarly, in the pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus (SE) model, BmK IT2 significantly prolonged the latency to onset of the SE, reduced the severity of SE and suppressed hippocampal c-Fos expression during SE.
Conclusions and implications: BmK IT2 showed anticonvulsant activity as it inhibited the widespread seizures induced by PTZ and pilocarpine-induced SE in rats. This activity might be due to the modulation of sodium channels in the hippocampus. Hence, BmK IT2 could be used as a novel tool to explore the molecular and pathological mechanisms of epilepsy with regard to the involvement of sodium channels.
Figures

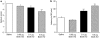
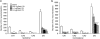
References
-
- Bai ZT, Zhang XY, Ji YH. Fos expression in rat spinal cord induced by peripheral injection of BmK I, an alpha-like scorpion neurotoxin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2003;192:78–85. - PubMed
-
- Bai ZT, Zhao R, Zhang XY, Chen J, Liu T, Ji YH. The epileptic seizures induced by BmK I, a modulator of sodium channels. Exp Neurol. 2006;197:167–176. - PubMed
-
- Barkai E, Grossman Y, Gutnick MJ. Long-term changes in neocortical activity after chemical kindling with systemic pentylenetetrazole: an in vitro study. J Neurophysiol. 1994;72:72–83. - PubMed
-
- Beleboni RO, Pizzo AB, Fontana ACK, Carolino ROG, Coutinho-Netto J, Santos WF. Spider and wasps neurotoxins: pharmacological and biochemical aspects. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004;17:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Browning RA.Effect of lesions on seizures in experimental animals Epilepsy and the Reticular Formation: The role of the Reticular Core in Convulsive Seizures 1987New York; 137–162.Alan R. Liss
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

