SWITCH: rationale, design, and implementation of a community, school, and family-based intervention to modify behaviors related to childhood obesity
- PMID: 18588706
- PMCID: PMC2474862
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-8-223
SWITCH: rationale, design, and implementation of a community, school, and family-based intervention to modify behaviors related to childhood obesity
Abstract
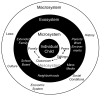
Background: Although several previous projects have attempted to address the issue of child obesity through school-based interventions, the overall effectiveness of school-based programs on health-related outcomes in youth has been poor. Thus, it has been suggested that multi-level interventions that aim to influence healthy lifestyle behaviors at the community, school and family levels may prove more successful in the prevention of childhood obesity.
Methods/design: This paper describes the rationale, design, and implementation of a community-, school-, and family-based intervention aimed at modifying key behaviors (physical activity, screen time (Internet, television, video games), and nutrition) related to childhood obesity among third through fifth graders in two mid-western cities. The intervention involves a randomized study of 10 schools (5 intervention and 5 control schools). The intervention is being conducted during the duration of the academic year - approximately 9 months - and includes baseline and post-intervention measurements of physical activity, dietary intake, screen time and body composition.
Discussion: We hope this report will be useful to researchers, public health professionals, and school administrators and health professionals (nurses and physical/health educators) seeking to develop similar prevention programs. It is obvious that more collaborative, inter-disciplinary, multi-level work is needed before a proven, effective intervention package to modify behaviors related to childhood obesity can be generally recommended. It is our hope that SWITCH is a step in that direction.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00685555.
Figures
References
-
- Nieto FJ, Szklo M, Comstock GW. Childhood weight and growth rate as predictors of adult mortality. Am J Epidemiol. 1992;136:210–213. - PubMed
-
- Bar-Or O, Foreyt J, Bouchard C, Brownell KD, Dietz WH, Ravussin E, Salbe AD, Schwenger S, St. Jeor S, Torun B. Physical activity, genetic, and nutritional considerations in childhood weight management. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1998;30:2–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical