Mitochondrial function and redox control in the aging eye: role of MsrA and other repair systems in cataract and macular degenerations
- PMID: 18588875
- PMCID: PMC2683477
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2008.05.018
Mitochondrial function and redox control in the aging eye: role of MsrA and other repair systems in cataract and macular degenerations
Abstract
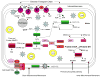
Oxidative stress occurs when the level of prooxidants exceeds the level of antioxidants in cells resulting in oxidation of cellular components and consequent loss of cellular function. Oxidative stress is implicated in wide range of age-related disorders including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Huntington's disease and the aging process itself. In the anterior segment of the eye, oxidative stress has been linked to lens cataract and glaucoma while in the posterior segment of the eye oxidative stress has been associated with macular degeneration. Key to many oxidative stress conditions are alterations in the efficiency of mitochondrial respiration resulting in superoxide (O(2)(-)) production. Superoxide production precedes subsequent reactions that form potentially more dangerous reactive oxygen species (ROS) species such as the hydroxyl radical (OH), hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)) and peroxynitrite (OONO(-)). The major source of ROS in the mitochondria, and in the cell overall, is leakage of electrons from complexes I and III of the electron transport chain. It is estimated that 0.2-2% of oxygen taken up by cells is converted to ROS, through mitochondrial superoxide generation, by the mitochondria. Generation of superoxide at complexes I and III has been shown to occur at both the matrix side of the inner mitochondrial membrane and the cytosolic side of the membrane. While exogenous sources of ROS such as UV light, visible light, ionizing radiation, chemotherapeutics, and environmental toxins may contribute to the oxidative milieu, mitochondria are perhaps the most significant contribution to ROS production affecting the aging process. In addition to producing ROS, mitochondria are also a target for ROS which in turn reduces mitochondrial efficiency and leads to the generation of more ROS in a vicious self-destructive cycle. Consequently, the mitochondria have evolved a number of antioxidant and key repair systems to limit the damaging potential of free oxygen radicals and to repair damaged proteins (Fig. 1). The aging eye appears to be at considerable risk from oxidative stress. This review will outline the potential role of mitochondrial function and redox balance in age-related eye diseases, and detail how the methionine sulfoxide reductase (Msr) protein repair system and other redox systems play key roles in the function and maintenance of the aging eye.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reactive Oxygen Species and the Aging Eye: Specific Role of Metabolically Active Mitochondria in Maintaining Lens Function and in the Initiation of the Oxidation-Induced Maturity Onset Cataract--A Novel Platform of Mitochondria-Targeted Antioxidants With Broad Therapeutic Potential for Redox Regulation and Detoxification of Oxidants in Eye Diseases.Am J Ther. 2016 Jan-Feb;23(1):e98-117. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0b013e3181ea31ff. Am J Ther. 2016. PMID: 21048433 Review.
-
Mitochondria induce oxidative stress, generation of reactive oxygen species and redox state unbalance of the eye lens leading to human cataract formation: disruption of redox lens organization by phospholipid hydroperoxides as a common basis for cataract disease.Cell Biochem Funct. 2011 Apr;29(3):183-206. doi: 10.1002/cbf.1737. Epub 2011 Mar 7. Cell Biochem Funct. 2011. PMID: 21381059
-
Oxidative stress and protein aggregation during biological aging.Exp Gerontol. 2001 Sep;36(9):1539-50. doi: 10.1016/s0531-5565(01)00139-5. Exp Gerontol. 2001. PMID: 11525876 Review.
-
Generation of reactive oxygen species in the anterior eye segment. Synergistic codrugs of N-acetylcarnosine lubricant eye drops and mitochondria-targeted antioxidant act as a powerful therapeutic platform for the treatment of cataracts and primary open-angle glaucoma.BBA Clin. 2016 Apr 19;6:49-68. doi: 10.1016/j.bbacli.2016.04.004. eCollection 2016 Dec. BBA Clin. 2016. PMID: 27413694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TXNL6 is a novel oxidative stress-induced reducing system for methionine sulfoxide reductase a repair of α-crystallin and cytochrome C in the eye lens.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 4;5(11):e15421. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015421. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21079812 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Involvement of transient receptor potential channels in ocular diseases: a narrative review.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Aug;10(15):839. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-6145. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36034986 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial tRNA-serine (AGY) m.C12264T mutation causes severe multisystem disease with cataracts.Discov Med. 2012 Feb;13(69):143-50. Discov Med. 2012. PMID: 22369973 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism of UVB irradiation induced-apoptosis in cataract.Mol Cell Biochem. 2015 Mar;401(1-2):87-95. doi: 10.1007/s11010-014-2294-x. Epub 2014 Dec 2. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25445170
-
Methionine sulfoxide and the methionine sulfoxide reductase system as modulators of signal transduction pathways: a review.Amino Acids. 2021 Jul;53(7):1011-1020. doi: 10.1007/s00726-021-03020-9. Epub 2021 Jun 18. Amino Acids. 2021. PMID: 34145481 Review.
-
Lens metabolomic profiling as a tool to understand cataractogenesis in Atlantic salmon and rainbow trout reared at optimum and high temperature.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 18;12(4):e0175491. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175491. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28419112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme. Arctic Pollution Issues. Oslo: Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme; 1998.
-
- Arner ES, Holmgren A. Physiological functions of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. Eur J Biochem. 2000;267(20):6102–6109. - PubMed
-
- Barja G. Free radicals and aging. Trends in Neurosciences. 2004;27:595–600. - PubMed
-
- Beal MF. Mitochondria take center stage in aging and neurodegeneration. Ann Neurol. 2005;58:495–505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

