Structural basis of guanine nucleotide exchange mediated by the T-cell essential Vav1
- PMID: 18589439
- PMCID: PMC2620086
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.05.024
Structural basis of guanine nucleotide exchange mediated by the T-cell essential Vav1
Abstract
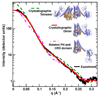
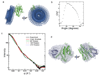
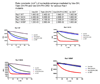
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) Vav1 plays an important role in T-cell activation and tumorigenesis. In the GEF superfamily, Vav1 has the ability to interact with multiple families of Rho GTPases. The structure of the Vav1 DH-PH-CRD/Rac1 complex to 2.6 A resolution reveals a unique intramolecular network of contacts between the Vav1 cysteine-rich domain (CRD) and the C-terminal helix of the Vav1 Dbl homology (DH) domain. These unique interactions stabilize the Vav1 DH domain for its intimate association with the Switch II region of Rac1 that is critical for the displacement of the guanine nucleotide. Small angle x-ray scattering (SAXS) studies support this domain arrangement for the complex in solution. Further, mutational analyses confirms that the atypical CRD is critical for maintaining both optimal guanine nucleotide exchange activity and broader specificity of Vav family GEFs. Taken together, the data outline the detailed nature of Vav1's ability to contact a range of Rho GTPases using a novel protein-protein interaction network.
Figures









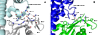
Similar articles
-
Remedial strategies in structural proteomics: expression, purification, and crystallization of the Vav1/Rac1 complex.Protein Expr Purif. 2007 May;53(1):51-62. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2006.10.027. Epub 2006 Dec 5. Protein Expr Purif. 2007. PMID: 17275330 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition and activation of Rho GTPases by Vav1 and Vav2 guanine nucleotide exchange factors.Biochemistry. 2005 May 3;44(17):6573-85. doi: 10.1021/bi047443q. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 15850391
-
Crucial structural role for the PH and C1 domains of the Vav1 exchange factor.EMBO Rep. 2008 Jul;9(7):655-61. doi: 10.1038/embor.2008.80. Epub 2008 May 30. EMBO Rep. 2008. PMID: 18511940 Free PMC article.
-
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor Tiam1: a Janus-faced molecule in cellular signaling.Cell Signal. 2014 Mar;26(3):483-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.034. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24308970 Review.
-
Vav family exchange factors: an integrated regulatory and functional view.Small GTPases. 2014;5(2):9. doi: 10.4161/21541248.2014.973757. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 25483299 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pak and Rac GTPases promote oncogenic KIT-induced neoplasms.J Clin Invest. 2013 Oct;123(10):4449-63. doi: 10.1172/JCI67509. Epub 2013 Sep 16. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 24091327 Free PMC article.
-
Function of the nucleotide exchange activity of vav1 in T cell development and activation.Sci Signal. 2009 Dec 15;2(101):ra83. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2000420. Sci Signal. 2009. PMID: 20009105 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of a RAC1-centred network is associated with Alzheimer's disease pathology and causes age-dependent neurodegeneration.Hum Mol Genet. 2020 Mar 27;29(5):817-833. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddz320. Hum Mol Genet. 2020. PMID: 31942999 Free PMC article.
-
Vav2 lacks Ca2+ entry-promoting scaffolding functions unique to Vav1 and inhibits T cell activation via Cdc42.J Cell Sci. 2020 Mar 13;133(5):jcs238337. doi: 10.1242/jcs.238337. J Cell Sci. 2020. PMID: 31974114 Free PMC article.
-
Lysine Acetylation Reshapes the Downstream Signaling Landscape of Vav1 in Lymphocytes.Cells. 2020 Mar 4;9(3):609. doi: 10.3390/cells9030609. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32143292 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rossman KL, Der CJ, Sondek J. GEF means go: turning on RHO GTPases with guanine nucleotide-exchange factors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:167–180. - PubMed
-
- Schapira V, Lazer G, Katzav S. Osteopontin is an oncogenic Vav1-but not wild-type Vav1-responsive gene: implications for fibroblast transformation. Cancer Res. 2006;66:6183–6191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

