barx1 is necessary for ectomesenchyme proliferation and osteochondroprogenitor condensation in the zebrafish pharyngeal arches
- PMID: 18590717
- PMCID: PMC2669285
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.06.004
barx1 is necessary for ectomesenchyme proliferation and osteochondroprogenitor condensation in the zebrafish pharyngeal arches
Abstract
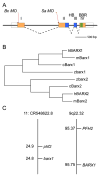
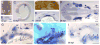
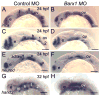
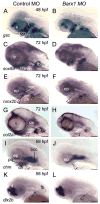
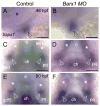
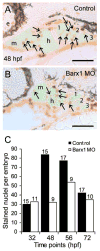
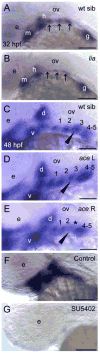
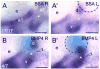
Barx1 modulates cellular adhesion molecule expression and participates in specification of tooth-types, but little is understood of its role in patterning the pharyngeal arches. We examined barx1 expression during zebrafish craniofacial development and performed a functional analysis using antisense morpholino oligonucleotides. Barx1 is expressed in the rhombencephalic neural crest, the pharyngeal arches, the pectoral fin buds and the gut in contrast to its paralogue barx2, which is most prominently expressed in the arch epithelium. Additionally, barx1 transient expression was observed in the posterior lateral line ganglia and developing trunk/tail. We show that Barx1 is necessary for proliferation of the arch osteochondrogenic progenitors, and that morphants exhibit diminished and dysmorphic arch cartilage elements due to reductions in chondrocyte differentiation and condensation. Attenuation of Barx1 results in lost arch expression of osteochondrogenic markers col2a1, runx2a and chondromodulin, as well as odontogenic marker dlx2b. Further, loss of barx1 positively influenced gdf5 and chordin, markers of jaw joint patterning. FGF signaling is required for maintaining barx1 expression, and that ectopic BMP4 induces expression of barx1 in the intermediate region of the second pharyngeal arch. Together, these results indicate an essential role for barx1 at early stages of chondrogenesis within the developing zebrafish viscerocranium.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Foxi transcription factors promote pharyngeal arch development by regulating formation of FGF signaling centers.Dev Biol. 2014 Jun 1;390(1):1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.03.004. Epub 2014 Mar 18. Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24650709 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish dlx2a contributes to hindbrain neural crest survival, is necessary for differentiation of sensory ganglia and functions with dlx1a in maturation of the arch cartilage elements.Dev Biol. 2008 Feb 1;314(1):59-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.11.005. Epub 2007 Nov 17. Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18158147
-
Tgfbeta3 regulation of chondrogenesis and osteogenesis in zebrafish is mediated through formation and survival of a subpopulation of the cranial neural crest.Mech Dev. 2010 Jul-Aug;127(7-8):329-44. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2010.04.003. Epub 2010 Apr 18. Mech Dev. 2010. PMID: 20406684
-
An essential role for zebrafish Fgfrl1 during gill cartilage development.Mech Dev. 2006 Dec;123(12):925-40. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2006.08.006. Epub 2006 Aug 24. Mech Dev. 2006. PMID: 17011755
-
DLX gene expression in the developing chick pharyngeal arches and relationship to endothelin signaling and avian jaw patterning.Dev Dyn. 2024 Feb;253(2):255-271. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.653. Epub 2023 Sep 14. Dev Dyn. 2024. PMID: 37706631 Review.
Cited by
-
prdm1a functions upstream of itga5 in zebrafish craniofacial development.Genesis. 2015 Mar-Apr;53(3-4):270-7. doi: 10.1002/dvg.22850. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Genesis. 2015. PMID: 25810090 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in Cell Proliferation and Craniofacial Phenotype of Closely Related Species in the Pupfish Genus Cyprinodon.J Hered. 2020 Apr 2;111(2):237-247. doi: 10.1093/jhered/esz074. J Hered. 2020. PMID: 31811714 Free PMC article.
-
A role for chemokine signaling in neural crest cell migration and craniofacial development.Dev Biol. 2009 Sep 1;333(1):161-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.06.031. Epub 2009 Jul 1. Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19576198 Free PMC article.
-
prdm1a Regulates sox10 and islet1 in the development of neural crest and Rohon-Beard sensory neurons.Genesis. 2010 Nov;48(11):656-66. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20673. Epub 2010 Nov 2. Genesis. 2010. PMID: 20836130 Free PMC article.
-
Redundant roles of PRDM family members in zebrafish craniofacial development.Dev Dyn. 2013 Jan;242(1):67-79. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.23895. Epub 2012 Nov 14. Dev Dyn. 2013. PMID: 23109401 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abu-Issa R, Smyth G, Smoak I, Yamamura K-i, Meyers EN. Fgf8 is required for pharyngeal arch and cardiovascular development in the mouse. Development. 2002;129:4613–4625. - PubMed
-
- Albertson RC, Yelick PC. Roles for fgf8 signaling in left-right patterning of the visceral organs and craniofacial skeleton. Dev Biol. 2005;283:310–21. - PubMed
-
- Angelo S, Lohr J, Lee KH, Ticho BS, Breitbart RE, Hill S, Yost HJ, Srivastava D. Conservation of sequence and expression of Xenopus and zebrafish dHAND during cardiac, branchial arch and lateral mesoderm development. Mech Dev. 2000;95:231–7. - PubMed
-
- Barlow AJ, Bogardi JP, Ladher R, Francis-West PH. Expression of chick Barx-1 and its differential regulation by FGF-8 and BMP signaling in the maxillary primordia. Dev Dyn. 1999;214:291–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

