Effects of subinhibitory concentrations of antibiotics on SOS and DNA repair gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 18591271
- PMCID: PMC2533449
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01599-07
Effects of subinhibitory concentrations of antibiotics on SOS and DNA repair gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
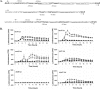
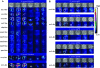
Reporter clones of Staphylococcus aureus with different SOS response- and DNA repair-associated promoter-lux gene fusion constructs were constructed to study the effects of sub-MICs of antibiotics on the transcription of the SOS and methyl mismatch repair (MMR) genes. Fluoroquinolones (FQs) upmodulated both the SOS and the MMR genes. The patterns of antibiotic-induced transcriptional modulation were altered in FQ-resistant mutants.
Figures
Similar articles
-
iTRAQ-based proteome analysis of fluoroquinolone-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2017 Mar;8:82-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2016.11.003. Epub 2016 Dec 27. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2017. PMID: 28039103
-
Phenotypic changes in ciprofloxacin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Res Microbiol. 2009 Dec;160(10):785-91. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2009.09.013. Epub 2009 Oct 7. Res Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19818400
-
N-acetylcysteine blocks SOS induction and mutagenesis produced by fluoroquinolones in Escherichia coli.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2019 Aug 1;74(8):2188-2196. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkz210. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31102529
-
Targeting the bacterial SOS response for new antimicrobial agents: drug targets, molecular mechanisms and inhibitors.Future Med Chem. 2021 Jan;13(2):143-155. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2020-0310. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Future Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33410707 Review.
-
Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus.Future Microbiol. 2007 Jun;2(3):323-34. doi: 10.2217/17460913.2.3.323. Future Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17661706 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of antibiotic treatments on the expression of the R plasmid tra genes and on the host innate immune activity during pRAS1 bearing Aeromonas hydrophila infection in zebrafish (Danio rerio).BMC Microbiol. 2012 Mar 19;12:37. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-37. BMC Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22429905 Free PMC article.
-
Vibrio cholerae triggers SOS and mutagenesis in response to a wide range of antibiotics: a route towards multiresistance.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 May;55(5):2438-41. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01549-10. Epub 2011 Feb 7. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21300836 Free PMC article.
-
Genomics of sponge-associated Streptomyces spp. closely related to Streptomyces albus J1074: insights into marine adaptation and secondary metabolite biosynthesis potential.PLoS One. 2014 May 12;9(5):e96719. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096719. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24819608 Free PMC article.
-
The physiology and genetics of bacterial responses to antibiotic combinations.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2022 Aug;20(8):478-490. doi: 10.1038/s41579-022-00700-5. Epub 2022 Mar 3. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35241807 Review.
-
A role for the bacterial GATC methylome in antibiotic stress survival.Nat Genet. 2016 May;48(5):581-6. doi: 10.1038/ng.3530. Epub 2016 Mar 21. Nat Genet. 2016. PMID: 26998690 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abou-Eisha, A. 2006. Evaluation of cytogenetic and DNA damage induced by the antibacterial drug, trimethoprim. Toxicol. In Vitro 20:601-607. - PubMed
-
- Adhikari, R. P., and R. P. Novick. 2005. Subinhibitory cerulenin inhibits staphylococcal exoprotein production by blocking transcription rather than by blocking secretion. Microbiology 151:3059-3069. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, K. L., C. Roberts, T. Disz, V. Vonstein, K. Hwang, R. Overbeek, P. D. Olson, S. J. Projan, and P. M. Dunman. 2006. Characterization of the Staphylococcus aureus heat shock, cold shock, stringent, and SOS responses and their effects on log-phase mRNA turnover. J. Bacteriol. 188:6739-6756. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bisognano, C., W. L. Kelley, T. Estoppey, P. Francois, J. Schrenzel, D. Li, D. P. Lew, D. C. Hooper, A. L. Cheung, and P. Vaudaux. 2004. A RecA-LexA-dependent pathway mediates ciprofloxacin-induced fibronectin binding in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biol. Chem. 279:9064-9071. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

