A rush to judgment on Th17
- PMID: 18591407
- PMCID: PMC2442627
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20072066
A rush to judgment on Th17
Abstract
Some immunologists have characterized T helper (Th)17 T cells as the master mediators of tissue damage in a variety of pathological conditions. New data now demonstrate that Th1 and Th17 T cells are independently capable of inducing disease in two established models of autoimmunity. Thus, the role of Th17 cytokines as the central mediators of pathological tissue damage seems to require clarification.
Figures
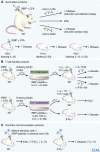
Comment on
-
Either a Th17 or a Th1 effector response can drive autoimmunity: conditions of disease induction affect dominant effector category.J Exp Med. 2008 Apr 14;205(4):799-810. doi: 10.1084/jem.20071258. Epub 2008 Apr 7. J Exp Med. 2008. PMID: 18391061 Free PMC article.
-
IL-12- and IL-23-modulated T cells induce distinct types of EAE based on histology, CNS chemokine profile, and response to cytokine inhibition.J Exp Med. 2008 Jul 7;205(7):1535-41. doi: 10.1084/jem.20080159. Epub 2008 Jun 23. J Exp Med. 2008. PMID: 18573909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steinman, L. 2007. A brief history of TH17, the first major revision in the TH1/TH2 hypothesis of T cell-mediated tissue damage. Nat. Med. 13:139–145. - PubMed
-
- Bettelli, E., M. Oukka, and V.K. Kuchroo. 2007. T(H)-17 cells in the circle of immunity and autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 8:345–350. - PubMed
-
- Coffman, R.L. 2006. Origins of the T(H)1-T(H)2 model: a personal perspective. Nat. Immunol. 7:539–541. - PubMed
-
- Billiau, A., H. Heremans, F. Vandekerckhove, R. Dijkmans, H. Sobis, E. Meulepas, and H. Carton. 1988. Enhancement of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in mice by antibodies against IFN-gamma. J. Immunol. 140:1506–1510. - PubMed
-
- Ferber, I.A., S. Brocke, C. Taylor-Edwards, W. Ridgway, C. Dinisco, L. Steinman, D. Dalton, and C.G. Fathman. 1996. Mice with a disrupted interferon-gamma gene are susceptible to the induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). J. Immunol. 156:5–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

