High expression of HIF1a is a predictor of clinical outcome in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas and correlated to PDGFA, VEGF, and bFGF
- PMID: 18592007
- PMCID: PMC2435004
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.08292
High expression of HIF1a is a predictor of clinical outcome in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas and correlated to PDGFA, VEGF, and bFGF
Abstract
Purpose: Pancreatic cancer still has one of the worst prognoses in gastrointestinal cancers with a 5-year survival rate of 5%, making it necessary to find markers or gene sets that would further classify patients into different risk categories and thus allow more individually adapted multimodality treatment regimens. In this study, we investigated the prognostic values of HIF1a, bFGF, VEGF, and PDGFA gene expressions as well as their interrelationships.
Experimental design: Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue samples were obtained from 41 patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma (age, 65; range, 34-85 years). After laser capture microdissection, direct quantitative real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction assays were performed in triplicates to determine HIF1a, PDGFA, VEGF, and bFGF gene expression levels. Multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis was used to assess the impact of HIF1a gene expression on prognosis.
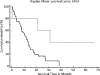
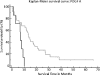
Results: HIF1a was significantly correlated to every gene we tested: bFGF (P = .04), VEGF (P = .02), and PDGFA (P = .03). Tumor size, P = .04, and high HIF1a mRNA expression (cutoff, 75th percentile) had a significant impact on survival, P = .009 (overall model fit, P = .02). High HIF1a expression had a sensitivity of 87.1% and a specificity of 55.6% for the diagnosis short (<6 months) versus long (6-60 months) survival.
Conclusions: Measuring PDGFA, bFGF, and HIF1a expression may contribute to a better understanding of the prognosis of patients with pancreatic cancer and may even play a crucial role for the distribution of patients to multimodal therapeutic regimens. Larger studies including patients treated with actual chemotherapeutics seem to be warranted.
Figures


References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:43–66. - PubMed
-
- Levi F, Lucchini F, Negri E, La Vecchia C. Pancreatic cancer mortality in Europe: the leveling of an epidemic. Pancreas. 2003;27:139–142. - PubMed
-
- Prenzel KL, Warnecke-Eberz U, Brabender J, Baldus SE, Bollschweiler E, Gutschow CA, Drebber U, Hoelscher AH, Schneider PM. Differential c-erbB-1 and c-erbB-2 mRNA expression in cancer of the pancreas compared with cancer of the papilla of Vater. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:437–442. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Couvelard A, O'Toole D, Turley H, Leek R, Sauvanet A, Degott C, Ruszniewski P, Belghiti J, Harris AL, Gatter K, et al. Microvascular density and hypoxia-inducible factor pathway in pancreatic endocrine tumours: negative correlation of microvascular density and VEGF expression with tumour progression. Br J Cancer. 2005;92:94–101. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sun HC, Qiu ZJ, Liu J, Sun J, Jiang T, Huang KJ, Yao M, Huang C. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and associated proteins in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and their impact on prognosis. Int J Oncol. 2007;30:1359–1367. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
