Temporal lobar predominance of TDP-43 neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions in Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 18592255
- PMCID: PMC3404722
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-008-0400-4
Temporal lobar predominance of TDP-43 neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions in Alzheimer disease
Abstract
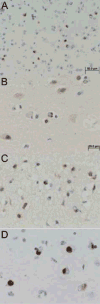
TAR DNA binding protein-43 (TDP-43) immunoreactive neuronal inclusions are detected in 20-30% of Alzheimer disease (AD) brains, but the distribution of this pathology has not been rigorously studied. In this report, we describe region-specific distribution and density of TDP-43 positive neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions (NCIs) in clinically demented individuals with high probability AD pathology, all with Braak neurofibrillary tangle stages of V or VI. Sections of hippocampus, amygdala, as well as temporal, frontal, and parietal neocortex, were analyzed with TDP-43 immunohistochemistry, and the density of NCIs was assessed using a semiquantitative scoring method. Of the 29 cases, six had TDP-43 positive NCIs in the amygdala only and seven had TDP-43 inclusions restricted to amygdala and hippocampus. In 16 cases, TDP-43 immunoreactivity was more widespread, affecting temporal, frontal or parietal neocortex. These findings indicate that medial temporal lobe limbic structures are vulnerable to TDP-43 pathology in advanced AD, and that the amygdala appears to be the most susceptible region. The distribution of the lesions in this cross-sectional analysis may suggest a progression of TDP-43 pathology in AD, with limbic structures in the medial temporal lobe affected first, followed by higher order association cortices.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson VE, Cairns NJ, Leigh PN. Involvement of the amygdala, dentate and hippocampus in motor neuron disease. J Neurol Sci. 1995;129 Suppl:75–78. - PubMed
-
- Barnes J, Whitwell JL, Frost C, Josephs KA, Rossor M, Fox NC. Measurements of the amygdala and hippocampus in pathologically confirmed Alzheimer disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Arch Neurol. 2006;63:1434–1439. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;82:239–259. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rub U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2003;24:197–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

