Microarray analysis of developing flax hypocotyls identifies novel transcripts correlated with specific stages of phloem fibre differentiation
- PMID: 18593690
- PMCID: PMC2701801
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcn110
Microarray analysis of developing flax hypocotyls identifies novel transcripts correlated with specific stages of phloem fibre differentiation
Abstract
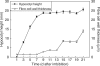
Background and aims: Hypocotyls are a commonly used model to study primary growth in plants, since post-germinative hypocotyls increase in size by cell elongation rather than cell division. Flax hypocotyls produce phloem fibres in bundles one to two cell layers thick, parallel to the protoxylem poles of the stele. Cell wall deposition within these cells occurs rapidly at a well-defined stage of development. The aim was to identify transcripts associated with distinct stages of hypocotyl and phloem fibre development.
Methods: Stages of flax hypocotyl development were defined by analysing hypocotyl length in relation to fibre secondary wall deposition. Selected stages of development were used in microarray analyses to identify transcripts involved in the transition from elongation to secondary cell wall deposition in fibres. Expression of specific genes was confirmed by qRT-PCR and by enzymatic assays.
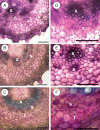
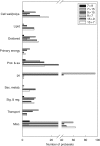
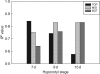
Key results: Genes enriched in the elongation phase included transcripts related to cell-wall modification or primary-wall deposition. Transcripts specifically enriched at the transition between elongation and secondary wall deposition included beta-galactosidase and arabinogalactan proteins. Later stages of wall development showed an increase in secondary metabolism-related transcripts, chitinases and glycosyl hydrolases including KORRIGAN. Microarray analysis also identified groups of transcription factors enriched at one or more stages of fibre development. Subsequent analysis of a differentially expressed beta-galactosidase confirmed that the post-elongation increase in beta-galactosidase enzyme activity was localized to phloem fibres.
Conclusions: Transcripts were identified associated with specific stages of hypocotyl development, in which phloem fibre cells were undergoing thickening of secondary walls. Temporal and spatial regulation of beta-galactosidase activity suggests a role for this enzyme in remodelling of flax bast fibre cell walls during secondary cell wall deposition.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evolutionary characterization and transcript profiling of β-tubulin genes in flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) during plant development.BMC Plant Biol. 2017 Dec 8;17(1):237. doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1186-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2017. PMID: 29221437 Free PMC article.
-
Microarray analysis of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) stems identifies transcripts enriched in fibre-bearing phloem tissues.Mol Genet Genomics. 2007 Aug;278(2):149-65. doi: 10.1007/s00438-007-0241-1. Epub 2007 May 15. Mol Genet Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17503083
-
LuFLA1PRO and LuBGAL1PRO promote gene expression in the phloem fibres of flax (Linum usitatissimum).Plant Cell Rep. 2013 Apr;32(4):517-28. doi: 10.1007/s00299-013-1383-8. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Plant Cell Rep. 2013. PMID: 23328964
-
[The development, differentiation and composition of flax fiber cells].Postepy Biochem. 2015;61(4):416-29. Postepy Biochem. 2015. PMID: 27048096 Review. Polish.
-
Secondary cell-wall assembly in flax phloem fibres: role of galactans.Planta. 2006 Jan;223(2):149-58. doi: 10.1007/s00425-005-0118-7. Epub 2005 Dec 16. Planta. 2006. PMID: 16362330 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome analysis of secondary-wall-enriched seed coat tissues of canola (Brassica napus L.).Plant Cell Rep. 2010 Apr;29(4):327-42. doi: 10.1007/s00299-010-0824-x. Epub 2010 Feb 10. Plant Cell Rep. 2010. PMID: 20145934
-
Studying Secondary Growth and Bast Fiber Development: The Hemp Hypocotyl Peeks behind the Wall.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Nov 18;7:1733. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01733. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27917184 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal regulation of cell-wall pectin methylesterase and peroxidase isoforms in cadmium-treated flax hypocotyl.Ann Bot. 2009 Dec;104(7):1363-72. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcp254. Epub 2009 Oct 8. Ann Bot. 2009. PMID: 19815572 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary characterization and transcript profiling of β-tubulin genes in flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) during plant development.BMC Plant Biol. 2017 Dec 8;17(1):237. doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1186-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2017. PMID: 29221437 Free PMC article.
-
History and prospects of flax genetic markers.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jan 15;15:1495069. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1495069. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 39881731 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ageeva MV, Petrovska B, Kieft H, Sal'nikov VV, Snegireva AV, van Dam JEG, et al. Intrusive growth of flax phloem fibers is of intercalary type. Planta. 2005;222:565–574. - PubMed
-
- de Alcantara PHN, Martim L, Silva CO, Dietrich SMC, Buckeridge MS. Purification of a beta-galactosidase from cotyledons of Hymenaea courbaril L. (Leguminosae): enzyme properties and biological function. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry. 2006;44:619–627. - PubMed
-
- Alexandre F, Morvan O, Gaffe J, Mareck A, Jauneau A, Dauchel H, et al. Pectin methylesterase pattern in flax seedlings during their development. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry. 1997;35:427–436.

