Identification of a second DNA binding site in the human Rad52 protein
- PMID: 18593704
- PMCID: PMC3259773
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M802204200
Identification of a second DNA binding site in the human Rad52 protein
Abstract
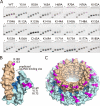
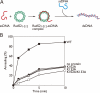
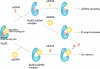
Rad52 plays essential roles in homology-dependent double-strand break repair. Various studies have established the functions of Rad52 in Rad51-dependent and Rad51-independent repair processes. However, the precise molecular mechanisms of Rad52 in these processes remain unknown. In the present study we have identified a novel DNA binding site within Rad52 by a structure-based alanine scan mutagenesis. This site is closely aligned with the putative single-stranded DNA binding site determined previously. Mutations in this site impaired the ability of the Rad52-single-stranded DNA complex to form a ternary complex with double-stranded DNA and subsequently catalyze the formation of D-loops. We found that Rad52 introduces positive supercoils into double-stranded DNA and that the second DNA binding site is essential for this activity. Our findings suggest that Rad52 aligns two recombining DNA molecules within the first and second DNA binding sites to stimulate the homology search and strand invasion processes.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Vital roles of the second DNA-binding site of Rad52 protein in yeast homologous recombination.J Biol Chem. 2011 May 20;286(20):17607-17. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.216739. Epub 2011 Mar 28. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21454474 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Rad52 amino-terminal DNA binding activity in DNA strand capture in homologous recombination.J Biol Chem. 2009 Nov 27;284(48):33275-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.057752. Epub 2009 Oct 6. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19812039 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstitution of the strand invasion step of double-strand break repair using human Rad51 Rad52 and RPA proteins.J Mol Biol. 2000 Nov 24;304(2):151-64. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4180. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 11080452
-
Emerging non-canonical roles for the Rad51-Rad52 interaction in response to double-strand breaks in yeast.Curr Genet. 2020 Oct;66(5):917-926. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01081-z. Epub 2020 May 12. Curr Genet. 2020. PMID: 32399607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Roles of RAD52 in Genome Maintenance.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jul 23;11(7):1038. doi: 10.3390/cancers11071038. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31340507 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of repeat length on Marcal1-dependent single-strand annealing in Drosophila.Genetics. 2023 Jan 12;223(1):iyac164. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyac164. Genetics. 2023. PMID: 36303322 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and mechanism of the Red recombination system of bacteriophage λ.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2019 Oct;147:33-46. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2019.03.005. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30904699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DSS1 interacts with and stimulates RAD52 to promote the repair of DSBs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jan 24;48(2):694-708. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz1052. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31799622 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Insights into RAD52's Structure, Function, and Druggability for Synthetic Lethality and Innovative Anticancer Therapies.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 17;15(6):1817. doi: 10.3390/cancers15061817. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic disruption of RAD52-ssDNA complexation via novel drug-like inhibitors.NAR Cancer. 2023 May 1;5(2):zcad018. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcad018. eCollection 2023 Jun. NAR Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37139244 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Daley, J. M., Palmbos, P. L., Wu, D., and Wilson, T. E. (2005) Annu. Rev. Genet. 39 431-451 - PubMed
-
- Sung, P., and Klein, H. (2006) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7739 -750 - PubMed
-
- Song, B., and Sung, P. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 27515895 -15904 - PubMed
-
- Sugiyama, T., and Kowalczykowski, S. C. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 27731663 -31672 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

