Methylation mediated silencing of MicroRNA-1 gene and its role in hepatocellular carcinogenesis
- PMID: 18593903
- PMCID: PMC2562630
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6655
Methylation mediated silencing of MicroRNA-1 gene and its role in hepatocellular carcinogenesis
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Methylation Mediated Silencing of MicroRNA-1 Gene and Its Role in Hepatocellular Carcinogenesis.Cancer Res. 2023 Dec 15;83(24):4181. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-2365. Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 38098455 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
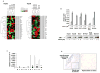
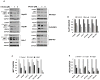
MicroRNAs (miR) are a class of small ( approximately 21 nucleotide) noncoding RNAs that, in general, negatively regulate gene expression. Some miRs harboring CGIs undergo methylation-mediated silencing, a characteristic of many tumor suppressor genes. To identify such miRs in liver cancer, the miRNA expression profile was analyzed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines treated with 5-azacytidine (DNA hypomethylating agent) and/or trichostatin A (histone deacetylase inhibitor). The results showed that these epigenetic drugs differentially regulate expression of a few miRs, particularly miR-1-1, in HCC cells. The CGI spanning exon 1 and intron 1 of miR-1-1 was methylated in HCC cell lines and in primary human HCCs but not in matching liver tissues. The miR-1-1 gene was hypomethylated and activated in DNMT1-/- HCT 116 cells but not in DNMT3B null cells, indicating a key role for DNMT1 in its methylation. miR-1 expression was also markedly reduced in primary human hepatocellular carcinomas compared with matching normal liver tissues. Ectopic expression of miR-1 in HCC cells inhibited cell growth and reduced replication potential and clonogenic survival. The expression of FoxP1 and MET harboring three and two miR-1 cognate sites, respectively, in their respective 3'-untranslated regions, was markedly reduced by ectopic miR-1. Up-regulation of several miR-1 targets including FoxP1, MET, and HDAC4 in primary human HCCs and down-regulation of their expression in 5-AzaC-treated HCC cells suggest their role in hepatocarcinogenesis. The inhibition of cell cycle progression and induction of apoptosis after re-expression of miR-1 are some of the mechanisms by which DNA hypomethylating agents suppress hepatocarcinoma cell growth.
Figures




Similar articles
-
miR-124 and miR-203 are epigenetically silenced tumor-suppressive microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma.Carcinogenesis. 2010 May;31(5):766-76. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp250. Epub 2009 Oct 20. Carcinogenesis. 2010. PMID: 19843643
-
Histone deacetylases activate hepatocyte growth factor signaling by repressing microRNA-449 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Gastroenterology. 2012 Sep;143(3):811-820.e15. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.05.033. Epub 2012 May 26. Gastroenterology. 2012. PMID: 22641068
-
MicroRNA-148a is silenced by hypermethylation and interacts with DNA methyltransferase 1 in hepatocellular carcinogenesis.Int J Oncol. 2014 Jun;44(6):1915-22. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2373. Epub 2014 Apr 8. Int J Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24714841
-
MicroRNAs: control and loss of control in human physiology and disease.World J Surg. 2009 Apr;33(4):667-84. doi: 10.1007/s00268-008-9836-x. World J Surg. 2009. PMID: 19030926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A miR image of stem cells and their lineages.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2012;99:175-99. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-387038-4.00007-0. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22365739 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetically regulated miR-449a enhances hepatitis B virus replication by targeting cAMP-responsive element binding protein 5 and modulating hepatocytes phenotype.Sci Rep. 2016 May 3;6:25389. doi: 10.1038/srep25389. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27138288 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-Mediated Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer.Pathol Oncol Res. 2017 Jan;23(1):1-12. doi: 10.1007/s12253-016-0101-6. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Pathol Oncol Res. 2017. PMID: 27590333 Review.
-
The role of microRNAs in liver cancer progression.Br J Cancer. 2011 Jan 18;104(2):235-40. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6606010. Epub 2010 Nov 23. Br J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21102580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-1 acts as a tumor suppressor microRNA by inhibiting angiogenesis-related growth factors in human gastric cancer.Gastric Cancer. 2018 Jan;21(1):41-54. doi: 10.1007/s10120-017-0721-x. Epub 2017 May 10. Gastric Cancer. 2018. PMID: 28493075 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA expression in ileal carcinoid tumors: downregulation of microRNA-133a with tumor progression.Mod Pathol. 2010 Mar;23(3):367-75. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2009.161. Epub 2009 Dec 25. Mod Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20037573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2557–76. - PubMed
-
- Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:857–66. - PubMed
-
- Kim VN. MicroRNA biogenesis: coordinated cropping and dicing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:376–85. - PubMed
-
- Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:102–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

