Loss of the SSeCKS/Gravin/AKAP12 gene results in prostatic hyperplasia
- PMID: 18593908
- PMCID: PMC2839164
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5619
Loss of the SSeCKS/Gravin/AKAP12 gene results in prostatic hyperplasia
Abstract
SSeCKS/Gravin/AKAP12 (SSeCKS) is a kinase scaffolding protein that encodes metastasis-suppressor activity through the suppression of Src-mediated oncogenic signaling and vascular endothelial growth factor expression. SSeCKS expression is down-regulated in Src- and Ras-transformed fibroblasts, in human cancer cell lines and in several types of human cancer, including prostate. Normal human and mouse prostates express abundant SSeCKS in secretory epithelial cells and, to a lesser extent, in the surrounding mesenchyme. Here, we show that the loss of SSeCKS results in prostatic hyperplasia in the anterior and ventral lobes as well as increased levels of apoptosis throughout the prostate. Dysplastic foci were observed less frequently but were associated with the loss of E-cadherin staining and the loss of high molecular weight cytokeratin-positive basal epithelial cells. SSeCKS-null prostate tissues expressed significantly higher relative levels of AKT(poS473) compared with wild-type controls, suggesting that SSeCKS attenuates phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase signaling. The data suggest that SSeCKS-null mice have increased susceptibility for oncogenic transformation in the prostate.
Figures

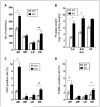
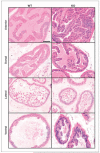
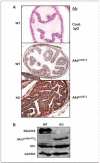
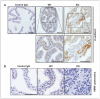
Similar articles
-
Carcinogen-induced squamous papillomas and oncogenic progression in the absence of the SSeCKS/AKAP12 metastasis suppressor correlate with FAK upregulation.Int J Cancer. 2011 Oct 15;129(8):2025-31. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25828. Epub 2011 Apr 1. Int J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21128249 Free PMC article.
-
The Src-suppressed C kinase substrate, SSeCKS, is a potential metastasis inhibitor in prostate cancer.Cancer Res. 2001 Jul 15;61(14):5644-51. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11454719
-
A role for SSeCKS, a major protein kinase C substrate with tumour suppressor activity, in cytoskeletal architecture, formation of migratory processes, and cell migration during embryogenesis.Histochem J. 2000 Jan;32(1):13-26. doi: 10.1023/a:1003950027529. Histochem J. 2000. PMID: 10805381
-
Suppression of tumor and metastasis progression through the scaffolding functions of SSeCKS/Gravin/AKAP12.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012 Dec;31(3-4):493-500. doi: 10.1007/s10555-012-9360-1. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012. PMID: 22684366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of SSeCKS/gravin/AKAP12 scaffolding proteins in the spaciotemporal control of signaling pathways in oncogenesis and development.Front Biosci. 2002 Aug 1;7:d1782-97. doi: 10.2741/A879. Front Biosci. 2002. PMID: 12133808 Review.
Cited by
-
Micro-RNA-186-5p inhibition attenuates proliferation, anchorage independent growth and invasion in metastatic prostate cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2018 Apr 13;18(1):421. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4258-0. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29653561 Free PMC article.
-
Prompt meningeal reconstruction mediated by oxygen-sensitive AKAP12 scaffolding protein after central nervous system injury.Nat Commun. 2014 Sep 17;5:4952. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5952. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 25229625 Free PMC article.
-
AKAP12 variant 1 knockout enhances vascular endothelial cell motility.J Vasc Res. 2025 Jul 18:1-24. doi: 10.1159/000547350. Online ahead of print. J Vasc Res. 2025. PMID: 40684770 Free PMC article.
-
Pivotal Role of AKAP12 in the Regulation of Cellular Adhesion Dynamics: Control of Cytoskeletal Architecture, Cell Migration, and Mitogenic Signaling.J Signal Transduct. 2012;2012:529179. doi: 10.1155/2012/529179. Epub 2012 Jun 28. J Signal Transduct. 2012. PMID: 22811901 Free PMC article.
-
SSeCKS/Akap12 suppresses metastatic melanoma lung colonization by attenuating Src-mediated pre-metastatic niche crosstalk.Oncotarget. 2018 Sep 11;9(71):33515-33527. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26067. eCollection 2018 Sep 11. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30323895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nauert J, Klauck T, Langeberg LK, Scott JD. Gravin, an autoantigen recognized by serum from myasthenia gravis patients, is a kinase scaffolding protein. Curr Biol. 1997;7:52–62. - PubMed
-
- Lin X, Gelman IH. Re-expression of the major protein kinase C substrate, SSeCKS, suppresses v-src-induced morphological transformation and tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 1997;57:2304–12. - PubMed
-
- Gelman IH. The role of the SSeCKS/Gravin/AKAP12 scaffolding proteins in the spaciotemporal control of signaling pathways in oncogenesis and development. Front Biosci. 2002;7:1797. - PubMed
-
- Su B, Zheng Q, Vaughan MM, Bu Y, Gelman IH. SSeCKS metastasis-suppressing activity in MatLyLu prostate cancer cells correlates with VEGF inhibition. Cancer Res. 2006;66:5599–607. - PubMed
-
- Xia W, Unger P, Miller L, Nelson J, Gelman IH. The Srcsuppressed C kinase substrate, SSeCKS, is a potential metastasis inhibitor in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2001;15:5644–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

