Combined inhibition of c-Src and epidermal growth factor receptor abrogates growth and invasion of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 18594011
- PMCID: PMC3428119
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-5226
Combined inhibition of c-Src and epidermal growth factor receptor abrogates growth and invasion of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Increased expression and/or activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis in many cancers, including head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Src family kinases, including c-Src, mediate a variety of intracellular or extracellular signals that contribute to tumor formation and progression. This study was undertaken to elucidate the role of c-Src in the growth and invasion of HNSCC and to determine the effects of combined targeting of EGFR and Src kinases in HNSCC cell lines.
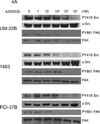
Experimental design: HNSCC cells were engineered to stably express a dominant-active form of c-Src and investigated in cell growth and invasion assays. The biochemical effects of combined treatment with the Src inhibitor AZD0530, a potent, orally active Src inhibitor with Bcr/Abl activity, and the EGFR kinase inhibitor gefitinib were examined, as well as the consequences of dual Src/EGFR targeting on the growth and invasion of a panel of HNSCC cell lines.
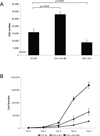
Results: HNSCC cells expressing dominant-active c-Src showed increased growth and invasion compared with vector-transfected controls. Combined treatment with AZD0530 and gefitinib resulted in greater inhibition of HNSCC cell growth and invasion compared with either agent alone.
Conclusions: These results suggest that increased expression and activation of c-Src promotes HNSCC progression where combined targeting of EGFR and c-Src may be an efficacious treatment approach.
Figures










References
-
- Leon X, Hitt R, Constenla M, et al. A retrospective analysis of the outcome of patients with recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck refractory to a platinum-based chemotherapy. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 2005;17:418–424. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter G, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:7709–7712. - PubMed
-
- Mendelsohn J, Baselga J. The EGF receptor family as targets for cancer therapy. Oncogene. 2000;19:6550–6565. - PubMed
-
- Rubin Grandis J, Melhem MF, Barnes EL, Tweardy DJ. Quantitative immunohistochemical analysis of transforming growth factor- alpha and epidermal growth factor receptor in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer. 1996;78:1284–1292. - PubMed
-
- Santini J, Formento JL, Francoual M, et al. Characterization, quantification, and potential clinical value of the epidermal growth factor receptor in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Head Neck. 1991;13:132–139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

