Structure of a beta1-adrenergic G-protein-coupled receptor
- PMID: 18594507
- PMCID: PMC2923055
- DOI: 10.1038/nature07101
Structure of a beta1-adrenergic G-protein-coupled receptor
Abstract
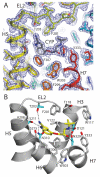
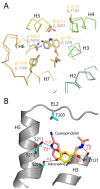
G-protein-coupled receptors have a major role in transmembrane signalling in most eukaryotes and many are important drug targets. Here we report the 2.7 A resolution crystal structure of a beta(1)-adrenergic receptor in complex with the high-affinity antagonist cyanopindolol. The modified turkey (Meleagris gallopavo) receptor was selected to be in its antagonist conformation and its thermostability improved by earlier limited mutagenesis. The ligand-binding pocket comprises 15 side chains from amino acid residues in 4 transmembrane alpha-helices and extracellular loop 2. This loop defines the entrance of the ligand-binding pocket and is stabilized by two disulphide bonds and a sodium ion. Binding of cyanopindolol to the beta(1)-adrenergic receptor and binding of carazolol to the beta(2)-adrenergic receptor involve similar interactions. A short well-defined helix in cytoplasmic loop 2, not observed in either rhodopsin or the beta(2)-adrenergic receptor, directly interacts by means of a tyrosine with the highly conserved DRY motif at the end of helix 3 that is essential for receptor activation.
Figures

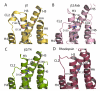
References
-
- Fredriksson R, Schioth HB. The repertoire of G-protein-coupled receptors in fully sequenced genomes. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005;67:1414–1425. - PubMed
-
- Hubbell WL, Altenbach C, Hubbell CM, Khorana HG. Rhodopsin structure, dynamics, and activation: A perspective from crystallography, site-directed spin labeling, sulfhydryl reactivity, and disulfide cross-linking. Adv. Protein Chem. 2003;63:243–290. - PubMed
-
- Foord SM, et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XLVI. G protein-coupled receptor list. Pharmaco.l Rev. 2005;57:279–288. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin JM, Schertler GF, Unger VM. An alpha-carbon template for the transmembrane helices in the rhodopsin family of G-protein-coupled receptors. J. Mol. Biol. 1997;272:144–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

