Clinical value of serum CA19-9 levels in evaluating resectability of pancreatic carcinoma
- PMID: 18595144
- PMCID: PMC2719240
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.3750
Clinical value of serum CA19-9 levels in evaluating resectability of pancreatic carcinoma
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the clinical value of serum CA19-9 levels in predicting the respectability of pancreatic carcinoma according to receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis.
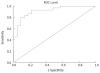
Methods: Serum CA19-9 levels were measured in 104 patients with pancreatic cancer which were possible to be resected according to the imaging. ROC curve was plotted for the CA19-9 levels. The point closest to the upper left-hand corner of the graph were chosen as the cut-off point. The sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values of CA19-9 at this cut-off point were calculated.
Results: Resectable pancreatic cancer was detected in 58 (55.77%) patients and unresectable pancreatic cancer was detected in 46 (44.23%) patients. The area under the ROC curve was 0.918 and 95% CI was 0.843-0.992. The CA19-9 level was 353.15 U/mL, and the sensitivity and specificity of CA19-9 at this cut-off point were 93.1% and 78.3%, respectively. The positive and negative predictive value was 84.38% and 90%, respectively.
Conclusion: Preoperative serum CA19-9 level is a useful marker for further evaluating the resectability of pancreatic cancer. Obviously increased serum levels of CA19-9 (> 353.15 U/mL) can be regarded as an ancillary parameter for unresectable pancreatic cancer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Preoperative Serum Carbohydrate Antigen 19-9 Levels Cannot Predict the Surgical Resectability of Pancreatic Cancer: A Meta-Analysis.Pathol Oncol Res. 2022 May 10;28:1610266. doi: 10.3389/pore.2022.1610266. eCollection 2022. Pathol Oncol Res. 2022. PMID: 35645620 Free PMC article.
-
Can preoperative CA19-9 and CEA levels predict the resectability of patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma?J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009 Dec;24(12):1869-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.05935.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 19686409
-
CA19-9 capability as predictor of pancreatic cancer resectability in a Spanish cohort.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Mar;47(3):1583-1588. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05245-5. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 31915999
-
Elevated serum CA19-9 level is a promising predictor for poor prognosis in patients with resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a pilot study.World J Surg Oncol. 2014 Jun 2;12:171. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-12-171. World J Surg Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24890327 Free PMC article.
-
Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 for differential diagnosis of pancreatic carcinoma and chronic pancreatitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Apr 14;21(14):4323-33. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4323. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25892884 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preoperative Serum Carbohydrate Antigen 19-9 Levels Cannot Predict the Surgical Resectability of Pancreatic Cancer: A Meta-Analysis.Pathol Oncol Res. 2022 May 10;28:1610266. doi: 10.3389/pore.2022.1610266. eCollection 2022. Pathol Oncol Res. 2022. PMID: 35645620 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma COL10A1 Level, a Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2024 Nov 6;17:949-959. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S474540. eCollection 2024. Onco Targets Ther. 2024. PMID: 39525356 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis and management of pancreatic cancer.Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2009 Dec;55(4):445-54. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2009. PMID: 19942828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated baseline CA19-9 levels correlate with adverse prognosis in patients with early- or advanced-stage pancreas cancer.Med Oncol. 2012 Dec;29(5):3101-7. doi: 10.1007/s12032-012-0278-9. Epub 2012 Jun 24. Med Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22729400 Free PMC article.
-
Survival benefit of neoadjuvant FOLFIRINOX for patients with borderline resectable pancreatic cancer.Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2024 May 31;28(2):229-237. doi: 10.14701/ahbps.23-107. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2024. PMID: 38296221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- Warshaw AL, Fernandez-del Castillo C. Pancreatic carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:455–465. - PubMed
-
- Tamm EP, Silverman PM, Charnsangavej C, Evans DB. Diagnosis, staging, and surveillance of pancreatic cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003;180:1311–1323. - PubMed
-
- Vargas R, Nino-Murcia M, Trueblood W, Jeffrey RB Jr. MDCT in Pancreatic adenocarcinoma: prediction of vascular invasion and resectability using a multiphasic technique with curved planar reformations. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;182:419–425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

