Effect of fragile histidine triad gene transduction on proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- PMID: 18595145
- PMCID: PMC2719241
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.3754
Effect of fragile histidine triad gene transduction on proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the inhibitory effects of human fragile histidine triad (FHIT) gene on cell proliferation and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma line Hep3B in vitro.
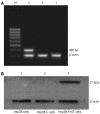
Methods: A recombinant pcDNA3.1 (+)/FHIT including the functional region of FHIT gene was constructed and transferred into human hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro. mRNA and protein expression of the FHIT gene in the transfected cells was detected by RT-PCR and Western blot, respectively. The effect of FHIT on proliferation was detected by MTT assay. Changes in cell cycle and apoptosis were assayed by flow cytometry. Five mice received subcutaneous transplantation of Hep3B-FHIT; 5 mice received subcutaneous transplantation of normal Hep3B and Hep3B-C as controls. The body weight of nude mice and tumor growth were measured.
Results: RT-PCR and Western blot analysis showed that the expression level of FHIT-mRNA and FHIT protein was higher in Hep3B cells after infection with pcDNA3.1 (+)/FHIT. The growth of Hep3B cells treated with pcDNA3.1 (+)/FHIT was significantly inhibited. The pcDNA3.1 (+)/FHIT-transfected Hep3B cells showed a significantly higher cell rate at G(0)-G(1) phase and increased apoptosis in comparison with controls (P < 0.05). The growth of transplanted tumor was inhibited markedly by FHIT. Tumors arising from the Hep3B-FHIT cells occurred much later than those arising from the Hep3B and Hep3B-C cells. The growth of Hep3B-FHIT cells was slow and the tumor volume was low.
Conclusion: Transduction of FHIT gene inhibits the growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells and induces cell apoptosis in vivo and in vitro.
Figures


References
-
- Ohta M, Inoue H, Cotticelli MG, Kastury K, Baffa R, Palazzo J, Siprashvili Z, Mori M, McCue P, Druck T, et al. The FHIT gene, spanning the chromosome 3p14.2 fragile site and renal carcinoma-associated t(3;8) breakpoint, is abnormal in digestive tract cancers. Cell. 1996;84:587–597. - PubMed
-
- Sozzi G, Veronese ML, Negrini M, Baffa R, Cotticelli MG, Inoue H, Tornielli S, Pilotti S, De Gregorio L, Pastorino U, et al. The FHIT gene 3p14.2 is abnormal in lung cancer. Cell. 1996;85:17–26. - PubMed
-
- Negrini M, Monaco C, Vorechovsky I, Ohta M, Druck T, Baffa R, Huebner K, Croce CM. The FHIT gene at 3p14.2 is abnormal in breast carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1996;56:3173–3179. - PubMed
-
- Sozzi G, Pastorino U, Moiraghi L, Tagliabue E, Pezzella F, Ghirelli C, Tornielli S, Sard L, Huebner K, Pierotti MA, et al. Loss of FHIT function in lung cancer and preinvasive bronchial lesions. Cancer Res. 1998;58:5032–5037. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

