Using joint activity schedules to promote peer engagement in preschoolers with autism
- PMID: 18595287
- PMCID: PMC2408340
- DOI: 10.1901/jaba.2008.41-237
Using joint activity schedules to promote peer engagement in preschoolers with autism
Abstract
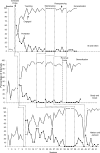
We assessed the use of a joint activity schedule to increase peer engagement for preschoolers with autism. We taught 3 dyads of preschoolers with autism to follow joint activity schedules that cued both members of the pair to play a sequence of interactive games together. Results indicated that joint activity schedules increased peer engagement and the number of games completed for all dyads. Schedule following was maintained without additional prompting when activities were resequenced and when new games were introduced for 2 of the 3 dyads.
Figures
References
-
- McClannahan L.E, Krantz P.J. Activity schedules for children with autism: Teaching independent behavior. Bethesda, MD: Woodbine House; 1999.
-
- Stevenson C.L, Krantz P.J, McClannahan L.E. Social interaction skills for children with autism: A script-fading procedure for nonreaders. Behavioral Interventions. 2000;15:1–20. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

