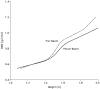
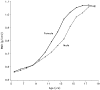
Effect of long-term corticosteroid use on bone mineral density in children: a prospective longitudinal assessment in the childhood Asthma Management Program (CAMP) study
- PMID: 18595975
- PMCID: PMC2928657
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2007-3381
Effect of long-term corticosteroid use on bone mineral density in children: a prospective longitudinal assessment in the childhood Asthma Management Program (CAMP) study
Abstract
Objective: Systemic corticosteroids are known to induce osteoporosis and increase the risk for fractures in adults and children. Inhaled corticosteroids have been shown to increase the risk for osteoporosis and fractures in adults at risk; however, long-term prospective studies of children to assess risks of multiple short courses of oral corticosteroids and chronic inhaled corticosteroids have not been performed. Thus, we assessed the effects of multiple short courses of oral corticosteroids and long-term inhaled corticosteroids on bone mineral accretion over a period of years.
Methods: This was a cohort follow-up study for a median of 7 years of children who had mild-to-moderate asthma and initially were randomly assigned into the Childhood Asthma Management Program trial. Serial dual-energy radiograph absorptiometry scans of the lumbar spine for bone mineral density were performed for all patients. Annual bone mineral accretion was calculated for 531 boys and 346 girls who had asthma and were aged 5 to 12 years at baseline (84% of the initial cohort).
Results: Oral corticosteroid bursts produced a dosage-dependent reduction in bone mineral accretion (0.052, 0.049, and 0.046 g/cm(2) per year) and an increase in risk for osteopenia (10%, 14%, and 21%) for 0, 1 to 4, and >or=5 courses, respectively, in boys but not girls. Cumulative inhaled corticosteroid use was associated with a small decrease in bone mineral accretion in boys but not girls but no increased risk for osteopenia.
Conclusions: Multiple oral corticosteroid bursts over a period of years can produce a dosage-dependent reduction in bone mineral accretion and increased risk for osteopenia in children with asthma. Inhaled corticosteroid use has the potential for reducing bone mineral accretion in male children progressing through puberty, but this risk is likely to be outweighed by the ability to reduce the amount of oral corticosteroids used in these children.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Do short courses of oral corticosteroids and use of inhaled corticosteroids affect bone health in children?Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Mar;5(3):132-3. doi: 10.1038/ncpendmet1072. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2009. PMID: 19229229
References
-
- Saag KG. Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am. 2003;32:135–157. - PubMed
-
- Lane NE, Lukert B. The science and therapy of glucocorticoid-induced bone loss. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am. 1998;27:465–483. - PubMed
-
- Walsh LJ, Lewis SA, Wong CA, et al. The impact of oral corticosteroid use on bone mineral density and vertebral fracture. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166:691–695. - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto H, Ishihara K, Hasegawa T, Umeda B, Niimi A, Hino M. Effects of inhaled corticosteroid and short courses or oral corticosteroids on bone mineral density in asthmatic patients: a 4 year longitudinal study. Chest. 2001;120:1468–1473. - PubMed
-
- van Staa TP, Cooper C, Leufkens HG, Bishop N. Children and the risk of fractures caused by oral corticosteroids. J Bone Miner Res. 2003;18:913–918. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01-HR-16046/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HR-16051/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HR-16044/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HR-16048/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HR-16045/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HR-16052/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR02719-14/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HR-16047/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HR-16049/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RR00036/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HR-16050/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000997/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR00051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR0099718-24/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical