Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1, yohimbine, and nitrergic modulation on sympathetic and parasympathetic activity in humans
- PMID: 18596108
- PMCID: PMC2536850
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00153.2008
Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1, yohimbine, and nitrergic modulation on sympathetic and parasympathetic activity in humans
Abstract
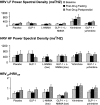
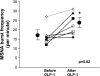
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), an incretin, which is used to treat diabetes mellitus in humans, inhibited vagal activity and activated nitrergic pathways. In rats, GLP-1 also increased sympathetic activity, heart rate, and blood pressure (BP). However, the effects of GLP-1 on sympathetic activity in humans are unknown. Our aims were to assess the effects of a GLP-1 agonist with or without alpha(2)-adrenergic or -nitrergic blockade on autonomic nervous functions in humans. In this double-blind study, 48 healthy volunteers were randomized to GLP-1-(7-36) amide, the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor N(G)-monomethyl-l-arginine acetate (l-NMMA), the alpha(2)-adrenergic antagonist yohimbine, or placebo (i.e., saline), alone or in combination. Hemodynamic parameters, plasma catecholamines, and cardiac sympathetic and parasympathetic modulation were measured by spectral analysis of heart rate. Thereafter, the effects of GLP-1-(7-36) amide on muscle sympathetic nerve activity (MSNA) were assessed by microneurography in seven subjects. GLP-1 increased (P = 0.02) MSNA but did not affect cardiac sympathetic or parasympathetic indices, as assessed by spectral analysis. Yohimbine increased plasma catecholamines and the low-frequency (LF) component of heart rate power spectrum, suggesting increased cardiac sympathetic activity. l-NMMA increased the BP and reduced the heart rate but did not affect the balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic activity. GLP-1 increases skeletal muscle sympathetic nerve activity but does not appear to affect cardiac sympathetic or parasympathetic activity in humans.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nitrergic contribution to gastric relaxation induced by glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in healthy adults.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 May;292(5):G1359-65. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00403.2006. Epub 2007 Feb 8. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17290009 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 and sympathetic stimulation on gastric accommodation in humans.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2007 Sep;19(9):716-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2007.00923.x. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2007. PMID: 17727392 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Nitric oxide and cardiac muscarinic control in humans.Hypertension. 2004 May;43(5):1023-8. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000126171.46645.f9. Epub 2004 Mar 22. Hypertension. 2004. PMID: 15037554 Clinical Trial.
-
Restoring the balance of the autonomic nervous system as an innovative approach to the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Mol Med. 2011 Sep-Oct;17(9-10):937-48. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00065. Epub 2011 May 20. Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21607292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacologic modulation of parasympathetic activity in heart failure.Heart Fail Rev. 2011 Mar;16(2):179-93. doi: 10.1007/s10741-010-9195-1. Heart Fail Rev. 2011. PMID: 20924667 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide on blood pressure profile, hydration, natriuresis in diabetic patients with severely impaired kidney function.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 29;14(1):5002. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55724-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38424466 Free PMC article.
-
Novel metabolic drugs and blood pressure: implications for the treatment of obese hypertensive patients?Curr Hypertens Rep. 2013 Oct;15(5):470-4. doi: 10.1007/s11906-013-0374-z. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2013. PMID: 23933756 Review.
-
GLP-1 and Underlying Beneficial Actions in Alzheimer's Disease, Hypertension, and NASH.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Sep 6;12:721198. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.721198. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34552561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GLP1R Attenuates Sympathetic Response to High Glucose via Carotid Body Inhibition.Circ Res. 2022 Mar 4;130(5):694-707. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.319874. Epub 2022 Feb 1. Circ Res. 2022. PMID: 35100822 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin- and glucagon-like peptide-1-induced changes in heart rate and vagosympathetic activity: why they matter.Diabetologia. 2013 Jun;56(6):1196-200. doi: 10.1007/s00125-013-2909-x. Epub 2013 Apr 13. Diabetologia. 2013. PMID: 23584434
References
-
- Andrews CN, Bharucha AE, Camilleri M, Low PA, Seide B, Burton D, Baxter K, Zinsmeister AR. Nitrergic contribution to gastric relaxation induced by glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in healthy adults. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 292: G1359–G1365, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. Heart rate variability: standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology [see comment]. Circulation 93: 1043–1065, 1996. - PubMed
-
- Baggio LL, Huang Q, Cao X, Drucker DJ. An albumin-exendin-4 conjugate engages central and peripheral circuits regulating murine energy and glucose homeostasis. Gastroenterology 134: 1137–1147, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Barragan JM, Eng J, Rodriguez R, Blazquez E. Neural contribution to the effect of glucagon-like peptide-1-(7-36) amide on arterial blood pressure in rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 277: E784–E791, 1999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

