Postnatal inflammation increases seizure susceptibility in adult rats
- PMID: 18596165
- PMCID: PMC3547980
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1901-08.2008
Postnatal inflammation increases seizure susceptibility in adult rats
Abstract
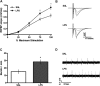
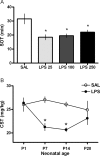
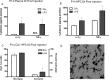
There are critical postnatal periods during which even subtle interventions can have long-lasting effects on adult physiology. We asked whether an immune challenge during early postnatal development can alter neuronal excitability and seizure susceptibility in adults. Postnatal day 14 (P14) male Sprague Dawley rats were injected with the bacterial endotoxin lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and control animals received sterile saline. Three weeks later, extracellular recordings from hippocampal slices revealed enhanced field EPSP slopes after Schaffer collateral stimulation and increased epileptiform burst-firing activity in CA1 after 4-aminopyridine application. Six to 8 weeks after postnatal LPS injection, seizure susceptibility was assessed in response to lithium-pilocarpine, kainic acid, and pentylenetetrazol. Rats treated with LPS showed significantly greater adult seizure susceptibility to all convulsants, as well as increased cytokine release and enhanced neuronal degeneration within the hippocampus after limbic seizures. These persistent increases in seizure susceptibility occurred only when LPS was given during a critical postnatal period (P7 and P14) and not before (P1) or after (P20). This early effect of LPS on adult seizures was blocked by concurrent intracerebroventricular administration of a tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) antibody and mimicked by intracerebroventricular injection of rat recombinant TNFalpha. Postnatal LPS injection did not result in permanent changes in microglial (Iba1) activity or hippocampal cytokine [IL-1beta (interleukin-1beta) and TNFalpha] levels, but caused a slight increase in astrocyte (GFAP) numbers. These novel results indicate that a single LPS injection during a critical postnatal period causes a long-lasting increase in seizure susceptibility that is strongly dependent on TNFalpha.
Figures



References
-
- Agrawal AK, Shapiro BH. Neonatal phenobarbital imprints overexpression of cytochromes P450 with associated increase in tumorigenesis and reduced life span. FASEB J. 2005;19:470–472. - PubMed
-
- Allan SM, Rothwell NJ. Cytokines and acute neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:734–744. - PubMed
-
- Allan SM, Tyrrell PJ, Rothwell NJ. Interleukin-1 and neuronal injury. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:629–640. - PubMed
-
- Annegers JF, Hauser WA, Beghi E, Nicolosi A, Kurland LT. The risk of unprovoked seizures after encephalitis and meningitis. Neurology. 1988;38:1407–1410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
