Early and late changes in the distal forelimb representation of the supplementary motor area after injury to frontal motor areas in the squirrel monkey
- PMID: 18596180
- PMCID: PMC2544457
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.90447.2008
Early and late changes in the distal forelimb representation of the supplementary motor area after injury to frontal motor areas in the squirrel monkey
Abstract
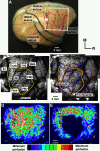
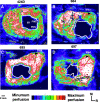
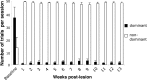
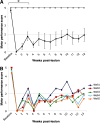
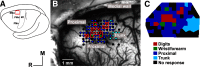
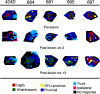
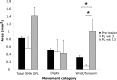
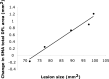
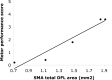
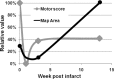
Neuroimaging studies in stroke survivors have suggested that adaptive plasticity occurs following stroke. However, the complex temporal dynamics of neural reorganization after injury make the interpretation of functional imaging studies equivocal. In the present study in adult squirrel monkeys, intracortical microstimulation (ICMS) techniques were used to monitor changes in representational maps of the distal forelimb in the supplementary motor area (SMA) after a unilateral ischemic infarct of primary motor (M1) and premotor distal forelimb representations (DFLs). In each animal, ICMS maps were derived at early (3 wk) and late (13 wk) postinfarct stages. Lesions resulted in severe deficits in motor abilities on a reach and retrieval task. Limited behavioral recovery occurred and plateaued at 3 wk postinfarct. At both early and late postinfarct stages, distal forelimb movements could still be evoked by ICMS in SMA at low current levels. However, the size of the SMA DFL changed after the infarct. In particular, wrist-forearm representations enlarged significantly between early and late stages, attaining a size substantially larger than the preinfarct area. At the late postinfarct stage, the expansion in the SMA DFL area was directly proportional to the absolute size of the lesion. The motor performance scores were positively correlated to the absolute size of the SMA DFL at the late postinfarct stage. Together, these data suggest that, at least in squirrel monkeys, descending output from M1 and dorsal and ventral premotor cortices is not necessary for SMA representations to be maintained and that SMA motor output maps undergo delayed increases in representational area after damage to other motor areas. Finally, the role of SMA in recovery of function after such lesions remains unclear because behavioral recovery appears to precede neurophysiological map changes.
Figures
References
-
- Aizawa H, Inase M, Mushiake H, Shima K, Tanji J. Reorganization of activity in the supplementary motor area associated with motor learning and functional recovery. Exp Brain Res 84: 668–671, 1991. - PubMed
-
- Boudrias MH, Belhaj-Saif A, Park MC, Cheney PD. Contrasting properties of motor output from the supplementary motor area and primary motor cortex in rhesus macaques. Cereb Cortex 16: 632–638, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Butefisch CM, Kleiser R, Seitz RJ. Post-lesional cerebral reorganisation: evidence from functional neuroimaging and transcranial magnetic stimulation. J Physiol 99: 437–454, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Cao Y, D'Olhaberriague L, Vikingstad EM, Levine SR, Welch KM. Pilot study of functional MRI to assess cerebral activation of motor function after poststroke hemiparesis. Stroke 29: 112–122, 1998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

