Large-scale quantitative LC-MS/MS analysis of detergent-resistant membrane proteins from rat renal collecting duct
- PMID: 18596208
- PMCID: PMC2544440
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.90650.2007
Large-scale quantitative LC-MS/MS analysis of detergent-resistant membrane proteins from rat renal collecting duct
Abstract
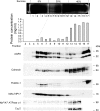
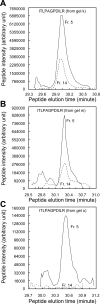
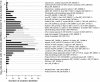
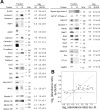
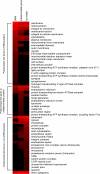
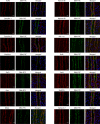
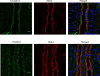
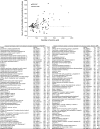
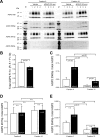
In the renal collecting duct, vasopressin controls transport of water and solutes via regulation of membrane transporters such as aquaporin-2 (AQP2) and the epithelial urea transporter UT-A. To discover proteins potentially involved in vasopressin action in rat kidney collecting ducts, we enriched membrane "raft" proteins by harvesting detergent-resistant membranes (DRMs) of the inner medullary collecting duct (IMCD) cells. Proteins were identified and quantified with LC-MS/MS. A total of 814 proteins were identified in the DRM fractions. Of these, 186, including several characteristic raft proteins, were enriched in the DRMs. Immunoblotting confirmed DRM enrichment of representative proteins. Immunofluorescence confocal microscopy of rat IMCDs with antibodies to DRM proteins demonstrated heterogeneity of raft subdomains: MAL2 (apical region), RalA (predominant basolateral labeling), caveolin-2 (punctate labeling distributed throughout the cells), and flotillin-1 (discrete labeling of large intracellular structures). The DRM proteome included GPI-anchored, doubly acylated, singly acylated, cholesterol-binding, and integral membrane proteins (IMPs). The IMPs were, on average, much smaller and more hydrophobic than IMPs identified in non-DRM-enriched IMCD. The content of serine 256-phosphorylated AQP2 was greater in DRM than in non-DRM fractions. Vasopressin did not change the DRM-to-non-DRM ratio of most proteins, whether quantified by tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS, n=22) or immunoblotting (n=6). However, Rab7 and annexin-2 showed small increases in the DRM fraction in response to vasopressin. In accord with the long-term goal of creating a systems-level analysis of transport regulation, this study has identified a large number of membrane-associated proteins expressed in the IMCD that have potential roles in vasopressin action.
Figures
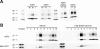

References
-
- Beausoleil SA, Villen J, Gerber SA, Rush J, Gygi SP. A probability-based approach for high-throughput protein phosphorylation analysis and site localization. Nat Biotechnol 24: 1285–1292, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Brown D, Roth J, Orci L. Lectin-gold cytochemistry reveals intercalated cell heterogeneity along rat kidney collecting ducts. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 248: C348–C356, 1985. - PubMed
-
- Brown DA Lipid rafts, detergent-resistant membranes, and raft targeting signals. Physiology (Bethesda) 21: 430–439, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Brown DA, Rose JK. Sorting of GPI-anchored proteins to glycolipid-enriched membrane subdomains during transport to the apical cell surface. Cell 68: 533–544, 1992. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

