The functional nitrite reductase activity of the heme-globins
- PMID: 18596228
- PMCID: PMC2556603
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-01-115261
The functional nitrite reductase activity of the heme-globins
Abstract
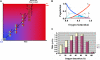
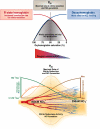
Hemoglobin and myoglobin are among the most extensively studied proteins, and nitrite is one of the most studied small molecules. Recently, multiple physiologic studies have surprisingly revealed that nitrite represents a biologic reservoir of NO that can regulate hypoxic vasodilation, cellular respiration, and signaling. These studies suggest a vital role for deoxyhemoglobin- and deoxymyoglobin-dependent nitrite reduction. Biophysical and chemical analysis of the nitrite-deoxyhemoglobin reaction has revealed unexpected chemistries between nitrite and deoxyhemoglobin that may contribute to and facilitate hypoxic NO generation and signaling. The first is that hemoglobin is an allosterically regulated nitrite reductase, such that oxygen binding increases the rate of nitrite conversion to NO, a process termed R-state catalysis. The second chemical property is oxidative denitrosylation, a process by which the NO formed in the deoxyhemoglobin-nitrite reaction that binds to other deoxyhemes can be released due to heme oxidation, releasing free NO. Third, the reaction undergoes a nitrite reductase/anhydrase redox cycle that catalyzes the anaerobic conversion of 2 molecules of nitrite into dinitrogen trioxide (N(2)O(3)), an uncharged molecule that may be exported from the erythrocyte. We will review these reactions in the biologic framework of hypoxic signaling in blood and the heart.
Figures


References
-
- Furchgott RF, Zawadzki JV. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980;288:373–376. - PubMed
-
- Palmer RM, Ashton DS, Moncada S. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from L-arginine. Nature. 1988;333:664–666. - PubMed
-
- Palmer RM, Ferrige AG, Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987;327:524–526. - PubMed
-
- Ignarro LJ, Byrns RE, Buga GM, Wood KS. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor from pulmonary artery and vein possesses pharmacologic and chemical properties identical to those of nitric oxide radical. Circ Res. 1987;61:866–879. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

