RACK1 regulates directional cell migration by acting on G betagamma at the interface with its effectors PLC beta and PI3K gamma
- PMID: 18596232
- PMCID: PMC2526680
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e08-04-0433
RACK1 regulates directional cell migration by acting on G betagamma at the interface with its effectors PLC beta and PI3K gamma
Abstract
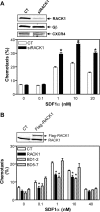
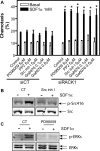
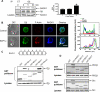
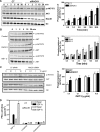
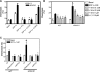
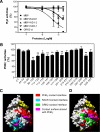
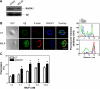
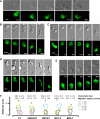
Migration of cells up the chemoattractant gradients is mediated by the binding of chemoattractants to G protein-coupled receptors and activation of a network of coordinated excitatory and inhibitory signals. Although the excitatory process has been well studied, the molecular nature of the inhibitory signals remains largely elusive. Here we report that the receptor for activated C kinase 1 (RACK1), a novel binding protein of heterotrimeric G protein betagamma (G betagamma) subunits, acts as a negative regulator of directed cell migration. After chemoattractant-induced polarization of Jurkat and neutrophil-like differentiated HL60 (dHL60) cells, RACK1 interacts with G betagamma and is recruited to the leading edge. Down-regulation of RACK1 dramatically enhances chemotaxis of cells, whereas overexpression of RACK1 or a fragment of RACK1 that retains G betagamma-binding capacity inhibits cell migration. Further studies reveal that RACK1 does not modulate cell migration through binding to other known interacting proteins such as PKC beta and Src. Rather, RACK1 selectively inhibits G betagamma-stimulated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase gamma (PI3K gamma) and phospholipase C (PLC) beta activity, due to the competitive binding of RACK1, PI3K gamma, and PLC beta to G betagamma. Taken together, these findings provide a novel mechanism of regulating cell migration, i.e., RACK1-mediated interference with G betagamma-dependent activation of key effectors critical for chemotaxis.
Figures
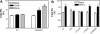
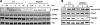
References
-
- Balkwill F. Cancer and the chemokine network. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2004;4:540–550. - PubMed
-
- Blackmer T., Larsen E. C., Takahashi M., Martin T. F., Alford S., Hamm H. E. G protein betagamma subunit-mediated presynaptic inhibition: regulation of exocytotic fusion downstream of Ca2+ entry. Science. 2001;292:293–297. - PubMed
-
- Buensuceso C. S., Obergfell A., Soriani A., Eto K., Kiosses W. B., Arias-Salgado E. G., Kawakami T., Shattil S. J. Regulation of outside-in signaling in platelets by integrin-associated protein kinase C beta. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:644–653. - PubMed
-
- Buensuceso C. S., Woodside D., Huff J. L., Plopper G. E., O'Toole T. E. The WD protein Rack1 mediates protein kinase C and integrin-dependent cell migration. J. Cell Sci. 2001;114:1691–1698. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

