Capture of AT-rich chromatin by ELYS recruits POM121 and NDC1 to initiate nuclear pore assembly
- PMID: 18596237
- PMCID: PMC2526682
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e08-01-0012
Capture of AT-rich chromatin by ELYS recruits POM121 and NDC1 to initiate nuclear pore assembly
Abstract
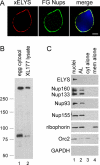
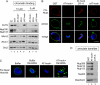
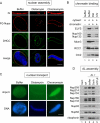
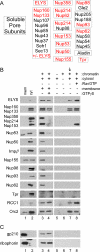
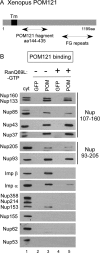
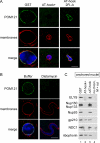
Assembly of the nuclear pore, gateway to the genome, from its component subunits is a complex process. In higher eukaryotes, nuclear pore assembly begins with the binding of ELYS/MEL-28 to chromatin and recruitment of the large critical Nup107-160 pore subunit. The choreography of steps that follow is largely speculative. Here, we set out to molecularly define early steps in nuclear pore assembly, beginning with chromatin binding. Point mutation analysis indicates that pore assembly is exquisitely sensitive to the change of only two amino acids in the AT-hook motif of ELYS. The dependence on AT-rich chromatin for ELYS binding is borne out by the use of two DNA-binding antibiotics. AT-binding Distamycin A largely blocks nuclear pore assembly, whereas GC-binding Chromomycin A(3) does not. Next, we find that recruitment of vesicles containing the key integral membrane pore proteins POM121 and NDC1 to the forming nucleus is dependent on chromatin-bound ELYS/Nup107-160 complex, whereas recruitment of gp210 vesicles is not. Indeed, we reveal an interaction between the cytoplasmic domain of POM121 and the Nup107-160 complex. Our data thus suggest an order for nuclear pore assembly of 1) AT-rich chromatin sites, 2) ELYS, 3) the Nup107-160 complex, and 4) POM121- and NDC1-containing membrane vesicles and/or sheets, followed by (5) assembly of the bulk of the remaining soluble pore subunits.
Figures


Comment in
- Mol Biol Cell. 19:3615.
References
-
- Alber F., et al. The molecular architecture of the nuclear pore complex. Nature. 2007;450:695–701. - PubMed
-
- Anand A., Chada K. In vivo modulation of Hmgic reduces obesity. Nat. Genet. 2000;24:377–380. - PubMed
-
- Anderson D. J., Hetzer M. W. Nuclear envelope formation by chromatin-mediated reorganization of the endoplasmic reticulum. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007;9:1160–1166. - PubMed
-
- Antonin W., Ellenberg J., Dultz E. Nuclear pore complex assembly through the cell cycle: regulation and membrane organization. FEBS Lett. 2008;582:2004–2016. - PubMed
-
- Antonin W., Franz C., Haselmann U., Antony C., Mattaj I. W. The integral membrane nucleoporin pom121 functionally links nuclear pore complex assembly and nuclear envelope formation. Mol. Cell. 2005;17:83–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

