Differential effects of luminal arginine and glutamine on metalloproteinase production in the postischemic gut
- PMID: 18596315
- PMCID: PMC3295226
- DOI: 10.1177/0148607108319806
Differential effects of luminal arginine and glutamine on metalloproteinase production in the postischemic gut
Abstract
Background: Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are a group of endopeptidases induced under inflammatory conditions in the intestine which possess the capacity to degrade components of the extracellular matrix. We have previously demonstrated that MMP-2 expression correlates with increased inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) production in the stomach and that iNOS is upregulated in the postischemic gut by the luminal nutrient arginine and repressed by luminal glutamine. We therefore hypothesized that arginine would enhance expression of MMP-2 in the postischemic gut.
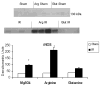
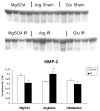
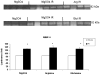
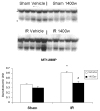
Methods: Jejunal sacs were created in rats at laparotomy and filled with either 60 mM glutamine, arginine, or magnesium sulfate (osmotic control) followed by 60 minutes of superior mesenteric artery occlusion (SMAO) and 6 hours of reperfusion and compared with shams. Jejunum was harvested, and membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP), MMP-2, and iNOS protein expression was determined by Western analysis and MMP-9 production by gelatin zymography.
Results: MMP-2, MT1-MMP, MMP-9, and iNOS were all increased after SMAO compared with shams. Arginine maintained while glutamine inhibited the increase in iNOS, MT1-MMP, and MMP-2 expression in the postischemic gut. Pretreatment of the arginine group with a selective iNOS inhibitor blunted the induction of MMP-2 in the postischemic gut. There was no differential modulation of MMP-9 by the luminal nutrients.
Conclusions: The arginine-induced upregulation of iNOS may contribute to increased activity of MT1-MMP and MMP-2. The mechanism for this differential regulation by arginine warrants further investigation.
Conflict of interest statement
No authors have a conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Differential induction of PPAR-gamma by luminal glutamine and iNOS by luminal arginine in the rodent postischemic small bowel.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006 Apr;290(4):G616-23. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00248.2005. Epub 2005 Oct 27. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16257923
-
Immune-enhancing enteral nutrients differentially modulate the early proinflammatory transcription factors mediating gut ischemia/reperfusion.J Trauma. 2005 Mar;58(3):455-61; discussion 461. doi: 10.1097/01.ta.0000153937.04932.59. J Trauma. 2005. PMID: 15761336
-
Effect of NOS inhibition on rat gastric matrix metalloproteinase production during endotoxemia.Shock. 2006 May;25(5):507-14. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000209543.83929.bd. Shock. 2006. PMID: 16680016
-
The immune-enhancing enteral agents arginine and glutamine differentially modulate gut barrier function following mesenteric ischemia/reperfusion.J Trauma. 2004 Dec;57(6):1150-6. doi: 10.1097/01.ta.0000151273.01810.e9. J Trauma. 2004. PMID: 15625443
-
Enteral glutamine: a novel mediator of PPARgamma in the postischemic gut.J Leukoc Biol. 2008 Sep;84(3):595-9. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1107764. Epub 2008 Apr 7. J Leukoc Biol. 2008. PMID: 18390929 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glutamine protects against apoptosis via downregulation of Sp3 in intestinal epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010 Dec;299(6):G1344-53. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00334.2010. Epub 2010 Sep 30. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20884886 Free PMC article.
-
Early anastomotic repair in the rat intestine is affected by transient preoperative mesenteric ischemia.J Gastrointest Surg. 2009 Jun;13(6):1099-106. doi: 10.1007/s11605-009-0827-5. Epub 2009 Feb 26. J Gastrointest Surg. 2009. PMID: 19242763
-
Gut homeostasis, injury, and healing: New therapeutic targets.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 May 7;28(17):1725-1750. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i17.1725. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35633906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of syndecan-1 shedding after hemorrhagic shock and resuscitation.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23530. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023530. Epub 2011 Aug 19. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21886795 Free PMC article.
-
Mucosal changes induced by ischemia-reperfusion injury in a jejunal loop transplanted in oropharynx.Intern Emerg Med. 2013 Jun;8(4):317-25. doi: 10.1007/s11739-011-0615-6. Epub 2011 May 8. Intern Emerg Med. 2013. PMID: 21553237
References
-
- Watanabe H, Nakanishi I, Yamashita K, Hayakawa T, Okada Y. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (92 kDa gelatinase/type iv collagenase) from U937 monoblastoid cells: correlation with cellular invasion. J Cell Sci. 1993;104(pt 4):991–999. - PubMed
-
- Keck T, Balcom JH, IV, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Antoniu BA, Warshaw AL. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 promotes neutrophil migration and alveolar capillary leakage in pancreatitis-associated lung injury in the rat. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:188–201. - PubMed
-
- Min D, Moore AG, Bain MA, Breit SN, Lyons JG. Activation of macrophage promatrix metalloproteinase-9 by lipopolysaccharide-associated proteinases. J Immunol. 2002;168:2449–2455. - PubMed
-
- Menshikov MY, Elizarova EP, Kudryashova E, et al. Plasmin-independent gelatinase B (matrix metalloproteinase-9) release by monocytes under the influence of urokinase. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2001;66:954–959. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

