Incidence of invasive ureaplasma in VLBW infants: relationship to severe intraventricular hemorrhage
- PMID: 18596706
- PMCID: PMC5334544
- DOI: 10.1038/jp.2008.98
Incidence of invasive ureaplasma in VLBW infants: relationship to severe intraventricular hemorrhage
Abstract
Objective: As Ureaplasmas may be pathogens in preterm infants, this study was conducted to determine the incidence of invasive disease with Ureaplasma parvum and Ureaplasma urealyticum and the relationship with adverse outcomes in a prospective cohort of very low birth weight (VLBW) infants.
Study design: DNA was extracted from the cord or venous blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples obtained from 313 VLBW infants. PCR was performed using primers for the mba gene to detect all 14 serovars and then repeated for all positive samples using species-specific primers.
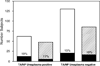
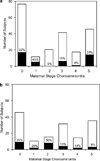
Result: Ureaplasma species were detected in serum and/or CSF samples from 74 of 313 (23.6%) infants. U. parvum was the predominant species (70%). Presence of Ureaplasma was significantly associated with elevated interleukin-1beta in cord blood (odds ratio (OR) 2.6, 1.05 to 6.45, P=0.039). Ureaplasma serum-positive infants had a 2.3-fold increased risk of intraventicular hemorrhage > or =grade 3 (OR 2.50; 1.06 to 5.89, P=0.036).
Conclusion: Invasive Ureaplasma occurs commonly in VLBW infants and may increase the risk for severe intraventricular hemorrhage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In utero exposure to Ureaplasma spp. is associated with increased rate of bronchopulmonary dysplasia and intraventricular hemorrhage in preterm infants.J Perinat Med. 2011 May;39(3):331-6. doi: 10.1515/jpm.2011.022. J Perinat Med. 2011. PMID: 21526978
-
Characterization of ureaplasmas isolated from preterm infants with and without bronchopulmonary dysplasia.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Sep;43(9):4852-4. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.9.4852-4854.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16145157 Free PMC article.
-
Ureaplasma bacteremia in very low birth weight infants in Brazil.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011 Dec;30(12):1052-5. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e31822a8662. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011. PMID: 21747320
-
Ureaplasma species: role in neonatal morbidities and outcomes.Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2014 Jan;99(1):F87-92. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2012-303351. Epub 2013 Aug 19. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2014. PMID: 23960141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ureaplasma species: role in diseases of prematurity.Clin Perinatol. 2010 Jun;37(2):393-409. doi: 10.1016/j.clp.2009.12.003. Clin Perinatol. 2010. PMID: 20569814 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Maternal Ureaplasma/Mycoplasma colonization during pregnancy and neurodevelopmental outcomes for preterm infants.Front Pediatr. 2022 Aug 15;10:893812. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.893812. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 36046478 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal azithromycin therapy for Ureaplasma intraamniotic infection delays preterm delivery and reduces fetal lung injury in a primate model.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2012 Dec;207(6):475.e1-475.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2012.10.871. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2012. PMID: 23111115 Free PMC article.
-
Ureaplasma Species Modulate Cytokine and Chemokine Responses in Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 22;20(14):3583. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143583. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31336668 Free PMC article.
-
Perinatal Ureaplasma Exposure Is Associated With Increased Risk of Late Onset Sepsis and Imbalanced Inflammation in Preterm Infants and May Add to Lung Injury.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Apr 2;9:68. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00068. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31001484 Free PMC article.
-
Intraamniotic infection with genital mycoplasmas exhibits a more intense inflammatory response than intraamniotic infection with other microorganisms in patients with preterm premature rupture of membranes.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010 Sep;203(3):211.e1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2010.03.035. Epub 2010 Aug 3. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010. PMID: 20678747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abele-Horn M, Peters J, Genzel-Boroviczeny O, Wolff C, Zimmermann A, Gottschling W. Vaginal Ureaplasma urealyticum colonization: influence on pregnancy outcome and neonatal morbidity. Infection. 1997;25:286–291. - PubMed
-
- Waites KB, Crouse DT, Philips JB, Canupp KC, Cassell GH. Ureaplasmal pneumonia and sepsis associated with persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Pediatrics. 1989;83:79–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

