Can early postpartum home visits by trained community health workers improve breastfeeding of newborns?
- PMID: 18596714
- PMCID: PMC2929160
- DOI: 10.1038/jp.2008.64
Can early postpartum home visits by trained community health workers improve breastfeeding of newborns?
Abstract
Objective: Whether postpartum visits by trained community health workers (CHWs), reduce newborn breastfeeding problems.
Method: Community health workers made antenatal and postpartum home visits promoting newborn care practices including breastfeeding. CHWs assessed neonates for adequacy of breastfeeding and provided hands-on support to mothers to establish breastfeeding. History and observation data of 3495 neonates were analyzed to assess effects of CHW visitation on feeding problems.
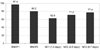
Result: Inappropriate breastfeeding position and attachment were the predominant problems (12 to 15%). Only 6% of newborns who received home visit by CHWs within 3 days had feeding difficulties, compared to 34% of those who did not (odds ratio: 7.66, 95% confidence interval (CI): 6.03 to 9.71, P=0.00). Latter group was 11.4 times (95% CI: 6.7 to 19.3, P=0.00) more likely to have feeding problems as late as days 6 to 7, than the former.
Conclusion: Counseling and hands-on support on breastfeeding techniques by trained workers within first 3 days of birth, should be part of community-based postpartum interventions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest arising through participation in the current study.
Figures
References
-
- Hanson LA. Breastfeeding provides passive and likely long-lasting active immunity. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1998;81:523–533. quiz 533-524, 537. - PubMed
-
- Oddy WH. Breastfeeding protects against illness and infection in infants and children: a review of the evidence. Breastfeed Rev. 2001;9:11–18. - PubMed
-
- Victora CG, Smith PG, Vaughan JP, Nobre LC, Lombardi C, Teixeira AM, et al. Infant feeding and deaths due to diarrhea. A case-control study. Am J Epidemiol. 1989;129:1032–1041. - PubMed
-
- Lucas A, Morley R, Cole TJ, Lister G, Leeson-Payne C. Breast milk and subsequent intelligence quotient in children born preterm. Lancet. 1992;339:261–264. - PubMed
-
- Jones G, Steketee RW, Black RE, Bhutta ZA, Morris SS. How many child deaths can we prevent this year? Lancet. 2003;362:65–71. - PubMed