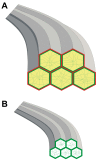
Distribution of basal membrane complex components in elongating lens fibers
- PMID: 18596883
- PMCID: PMC2442472
Distribution of basal membrane complex components in elongating lens fibers
Abstract
Purpose: To localize specific components of the Basal Membrane Complex (BMC) of elongating lens fibers at defined points in their migration to the posterior sutures.
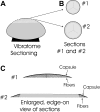
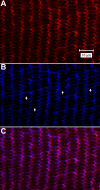
Methods: Normal, juvenile (4-6 week old) Sprague-Dawley rat lenses (n=46) were utilized. Lenses were either decapsulated to obtain whole mounts of lens capsules or sectioned with a vibrating knife microtome. Sections (100 microm thick) were cut parallel to the equatorial plane, beginning at the posterior pole. On both sections and whole mounts, F-actin was localized using phalloidin-FITC while myosin, cadherins, and beta1 integrin were localized using immunofluorescent labeling. Specimens were visualized on a laser scanning confocal microscope.
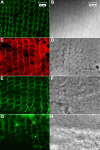
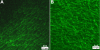
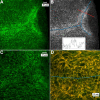
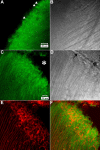
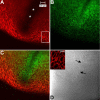
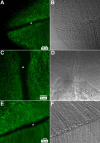
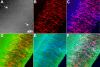
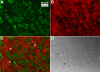
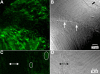
Results: F-actin labeling in the equatorial and peri-sutural regions was predominately localized to the periphery of basal fiber ends (consistent with our prior results). At sutures, labeling for F-actin in the BMC was rearranged into numerous small profiles. Furthermore, labeling intensity for F-actin was increased at sutures. Myosin was present in the BMC in all locations examined as a diffuse plaque at fiber ends. Similarly, beta1 integrin was also distributed throughout the BMC within the actin-rich borders in all regions except adjacent to and at the suture branches. In that location immunofluorescence for beta1 integrin appeared to be reduced. In the equatorial, lateral-posterior, and peri-sutural regions, cadherin showed strong localization around the periphery of basal fiber ends. However, cadherin labeling was markedly reduced in the BMC as fibers detached from the capsule and abutted to form sutures (i.e. in the sutural region). Cadherin was concentrated along the short faces of elongating fiber mid-segments.
Conclusions: It appears that F-actin, cadherin and beta1 integrin components of the BMC undergo controlled rearrangements in the final stages of migration and detachment from the capsule.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Abnormal fiber end migration in Royal College of Surgeons rats during posterior subcapsular cataract formation.Mol Vis. 2010 Jul 31;16:1453-66. Mol Vis. 2010. PMID: 20806082 Free PMC article.
-
Morphology and organization of posterior fiber ends during migration.Mol Vis. 2003 Apr 16;9:119-28. Mol Vis. 2003. PMID: 12707642
-
Molecular architecture of the lens fiber cell basal membrane complex.J Cell Sci. 1999 Jul;112 ( Pt 13):2155-65. doi: 10.1242/jcs.112.13.2155. J Cell Sci. 1999. PMID: 10362545
-
The ultrastructure of epithelial and fiber cells in the crystalline lens.Int Rev Cytol. 1995;163:305-50. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62213-5. Int Rev Cytol. 1995. PMID: 8522422 Review.
-
Sutures of the crystalline lens: a review.Scan Electron Microsc. 1984;(Pt 3):1369-78. Scan Electron Microsc. 1984. PMID: 6390664 Review.
Cited by
-
Basal membrane complex architecture is disrupted during posterior subcapsular cataract formation in Royal College of Surgeons rats.Mol Vis. 2014 Dec 31;20:1777-95. eCollection 2014. Mol Vis. 2014. PMID: 25593506 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive Optical Two-Photon Fluorescence Microscopy Probes Cellular Organization of Ocular Lenses In Vivo.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023 Jun 1;64(7):20. doi: 10.1167/iovs.64.7.20. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023. PMID: 37306987 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular mechanisms underlying lens fiber elongation.Exp Eye Res. 2017 Mar;156:41-49. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2016.03.016. Epub 2016 Mar 23. Exp Eye Res. 2017. PMID: 27015931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abnormal fiber end migration in Royal College of Surgeons rats during posterior subcapsular cataract formation.Mol Vis. 2010 Jul 31;16:1453-66. Mol Vis. 2010. PMID: 20806082 Free PMC article.
-
β1 integrin as the integrating component in cell-cell cooperation for maintenance of lens transparency.Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2013 Nov;453:297-9. doi: 10.1134/S1607672913060069. Epub 2014 Jan 3. Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2013. PMID: 24385100 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bassnett S, Missey H, Vucemilo I. Molecular architecture of the lens fiber cell basal membrane complex. J Cell Sci. 1999;112:2155–65. - PubMed
-
- Menko AS, Philip NJ. Beta 1 integrins in epithelial tissues: a unique distribution in the lens. Exp Cell Res. 1995;218:516–21. - PubMed
-
- Menko S, Philp N, Veneziale B, Walker J. Integrins and development: how might these receptors regulate differentiation of the lens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998;842:36–41. - PubMed
-
- Ferreira-Cornwell MC, Veneziale RW, Grunwald GB, Menko AS. N-cadherin function is required for differentiation-dependent cytoskeletal reorganization in lens cells in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 2000;256:237–47. - PubMed
-
- Zelenka PS. Regulation of cell adhesion and migration in lens development. Int J Dev Biol. 2004;48:857–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
