Quality of life after sentinel lymph node biopsy or axillary lymph node dissection in stage I/II breast cancer patients: a prospective longitudinal study
- PMID: 18597146
- PMCID: PMC2518082
- DOI: 10.1245/s10434-008-9996-9
Quality of life after sentinel lymph node biopsy or axillary lymph node dissection in stage I/II breast cancer patients: a prospective longitudinal study
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer patients' quality of life (QoL) after surgery has been reported to improve significantly over time. Little is known about QoL recovery after sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) in comparison to axillary lymph node dissection (ALND).
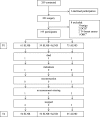
Methods: 175 of 195 stage I/II breast cancer patients completed the EORTC QLQ-C30: one day before surgery (T0) and after 6 (T1), 26 (T2), 52 (T3) and 104 (T4) weeks. Of these, 54 patients underwent SLNB, 56 SLNB+ALND and 65 ALND. General linear models and paired T-tests between T0-T4 and T1-T4 were computed. Complications, radiotherapy and systemic therapy were added to the model.
Results: Significant time effects were found on physical, role and emotional functioning. Physical and role functioning decreased between T0 and T1. At T4, SLNB patients' functioning had increased to their T0 level; ALND (+/- SLNB) patients' functioning had increased, but had not improved to T0 level. Emotional functioning increased linearly between T0 and T4. At T4, emotional functioning was significantly higher in all groups as compared with T0. No significant group or interaction (time x group) effects were found. Complications and chemotherapy had a significant negative effect on role, emotional and cognitive functioning. Complications had a significant effect on social functioning also. Effect sizes varied between 0.00 and 0.06.
Conclusion: Two years post surgery, breast cancer patients' QoL is comparable to that shortly before surgery. Women rated their emotional functioning as even better. SLNB is not associated with a better QoL than ALND. However, undergoing systemic therapy and/or experiencing complications affects QoL negatively.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical