Sparse estimation automatically selects voxels relevant for the decoding of fMRI activity patterns
- PMID: 18598768
- PMCID: PMC3158033
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.05.050
Sparse estimation automatically selects voxels relevant for the decoding of fMRI activity patterns
Abstract
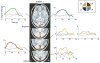
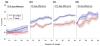
Recent studies have used pattern classification algorithms to predict or decode task parameters from individual fMRI activity patterns. For fMRI decoding, it is important to choose an appropriate set of voxels (or features) as inputs to the decoder, since the presence of many irrelevant voxels could lead to poor generalization performance, a problem known as overfitting. Although individual voxels could be chosen based on univariate statistics, the resulting set of voxels could be suboptimal if correlations among voxels carry important information. Here, we propose a novel linear classification algorithm, called sparse logistic regression (SLR), that automatically selects relevant voxels while estimating their weight parameters for classification. Using simulation data, we confirmed that SLR can automatically remove irrelevant voxels and thereby attain higher classification performance than other methods in the presence of many irrelevant voxels. SLR also proved effective with real fMRI data obtained from two visual experiments, successfully identifying voxels in corresponding locations of visual cortex. SLR-selected voxels often led to better performance than those selected based on univariate statistics, by exploiting correlated noise among voxels to allow for better pattern separation. We conclude that SLR provides a robust method for fMRI decoding and can also serve as a stand-alone tool for voxel selection.
Figures


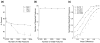



Similar articles
-
Comparison of multivariate classifiers and response normalizations for pattern-information fMRI.Neuroimage. 2010 Oct 15;53(1):103-18. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.05.051. Epub 2010 May 23. Neuroimage. 2010. PMID: 20580933 Free PMC article.
-
Combining multivariate voxel selection and support vector machines for mapping and classification of fMRI spatial patterns.Neuroimage. 2008 Oct 15;43(1):44-58. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.06.037. Epub 2008 Jul 11. Neuroimage. 2008. PMID: 18672070
-
Multiclass fMRI data decoding and visualization using supervised self-organizing maps.Neuroimage. 2014 Aug 1;96:54-66. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.02.006. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Neuroimage. 2014. PMID: 24531045
-
Modeling correlated noise is necessary to decode uncertainty.Neuroimage. 2018 Oct 15;180(Pt A):78-87. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.08.015. Epub 2017 Aug 8. Neuroimage. 2018. PMID: 28801251 Review.
-
Encoding and decoding in fMRI.Neuroimage. 2011 May 15;56(2):400-10. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.07.073. Epub 2010 Aug 4. Neuroimage. 2011. PMID: 20691790 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Decoding sequence learning from single-trial intracranial EEG in humans.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28630. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028630. Epub 2011 Dec 9. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22174850 Free PMC article.
-
Conducting decoded neurofeedback studies.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2021 Aug 6;16(8):838-848. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsaa063. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 32367138 Free PMC article.
-
Pain Control by Co-adaptive Learning in a Brain-Machine Interface.Curr Biol. 2020 Oct 19;30(20):3935-3944.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.07.066. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Curr Biol. 2020. PMID: 32795441 Free PMC article.
-
Time-dependent neural arbitration between cue associative and episodic fear memories.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 21;15(1):8706. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52733-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39433735 Free PMC article.
-
Group analysis and classification of working memory task conditions using electroencephalogram cortical currents during an n-back task.Front Neurosci. 2023 Oct 24;17:1222749. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1222749. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37942143 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Attias H. Inferring parameters and structure of latent variable models by variational Bayes. Proc. 15th Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence; Morgan Kaufmann Pub; 1999. pp. 21–30.
-
- Averbeck BB, Latham PE, Pouget A. Neural correlations, population coding and computation. Nat Rev, Neurosci. 2006;7:358–366. - PubMed
-
- Baker CI, Hutchison TL, Kanwisher N. Does the fusiform face area contain subregions highly selective for nonfaces? Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:3–4. - PubMed
-
- Bishop C, Tipping ME. Variational relevance vector machines. Proceedings of the 16th Conference in Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence; 2000. pp. 46–53.
-
- Bishop C. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Springer; New York: 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

