Menin critically links MLL proteins with LEDGF on cancer-associated target genes
- PMID: 18598942
- PMCID: PMC2692591
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.05.003
Menin critically links MLL proteins with LEDGF on cancer-associated target genes
Abstract
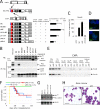
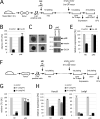
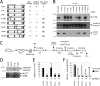
Menin displays the unique ability to either promote oncogenic function in the hematopoietic lineage or suppress tumorigenesis in the endocrine lineage; however, its molecular mechanism of action has not been defined. We demonstrate here that these discordant functions are unified by menin's ability to serve as a molecular adaptor that physically links the MLL (mixed-lineage leukemia) histone methyltransferase with LEDGF (lens epithelium-derived growth factor), a chromatin-associated protein previously implicated in leukemia, autoimmunity, and HIV-1 pathogenesis. LEDGF is required for both MLL-dependent transcription and leukemic transformation. Conversely, a subset of menin mutations in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 patients abrogate interaction with LEDGF while preserving MLL interaction but nevertheless compromise MLL/menin-dependent functions. Thus, LEDGF critically associates with MLL and menin at the nexus of transcriptional pathways that are recurrently targeted in diverse diseases.
Figures

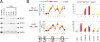


Comment in
-
A MENage à Trois in leukemia.Cancer Cell. 2008 Jul 8;14(1):3-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.06.009. Cancer Cell. 2008. PMID: 18598937
References
-
- Ahuja HG, Hong J, Aplan PD, Tcheurekdjian L, Forman SJ, Slovak ML. t(9;11)(p22;p15) in acute myeloid leukemia results in a fusion between NUP98 and the gene encoding transcriptional coactivators p52 and p75-lens epithelium-derived growth factor (LEDGF) Cancer Res. 2000;60:6227–6229. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Venegas R, Avramova Z. Two Arabidopsis homologs of the animal trithorax genes: a new structural domain is a signature feature of the trithorax gene family. Gene. 2001;271:215–221. - PubMed
-
- Balogh K, Racz K, Patocs A, Hunyady L. Menin and its interacting proteins: elucidation of menin function. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2006;17:357–364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

