Resveratrol delays age-related deterioration and mimics transcriptional aspects of dietary restriction without extending life span
- PMID: 18599363
- PMCID: PMC2538685
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2008.06.011
Resveratrol delays age-related deterioration and mimics transcriptional aspects of dietary restriction without extending life span
Abstract
A small molecule that safely mimics the ability of dietary restriction (DR) to delay age-related diseases in laboratory animals is greatly sought after. We and others have shown that resveratrol mimics effects of DR in lower organisms. In mice, we find that resveratrol induces gene expression patterns in multiple tissues that parallel those induced by DR and every-other-day feeding. Moreover, resveratrol-fed elderly mice show a marked reduction in signs of aging, including reduced albuminuria, decreased inflammation, and apoptosis in the vascular endothelium, increased aortic elasticity, greater motor coordination, reduced cataract formation, and preserved bone mineral density. However, mice fed a standard diet did not live longer when treated with resveratrol beginning at 12 months of age. Our findings indicate that resveratrol treatment has a range of beneficial effects in mice but does not increase the longevity of ad libitum-fed animals when started midlife.
Figures
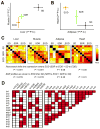
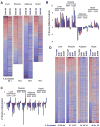

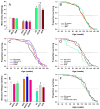
References
-
- Barger JL, Kayo T, Vann JM, Arias EB, Wang J, Hacker TA, Wang Y, Raederstorff D, Morrow JD, Leeuwenburgh C, Allison DB, Saupe KW, Cartee GD, Weindruch R, Prolla TA. A low dose of dietary resveratrol partially mimics caloric restriction and retards aging parameters in mice. PLoS ONE. 2008;3:e2264. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barger JL, Walford RL, Weindruch R. The retardation of aging by caloric restriction: its significance in the transgenic era. Exp Gerontol. 2003;38:1343–1351. - PubMed
-
- Bass TM, Weinkove D, Houthoofd K, Gems D, Partridge L. Effects of resveratrol on lifespan in Drosophila melanogaster and Caenorhabditis elegans. Mech Ageing Dev. 2007;128:546–552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL077256/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HD034089/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD034089/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AG000368/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- 2R01EY011733/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM068072/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019972/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 HD034089/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- AG19972/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG19719/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019719/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- SP30DK072437/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG028730/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL077256/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY011733/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR046121/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM068072/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

