Double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase mediates induction of interleukin-8 expression by deoxynivalenol, Shiga toxin 1, and ricin in monocytes
- PMID: 18599499
- PMCID: PMC2721672
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfn128
Double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase mediates induction of interleukin-8 expression by deoxynivalenol, Shiga toxin 1, and ricin in monocytes
Abstract
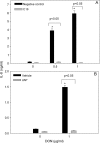
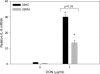
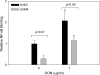
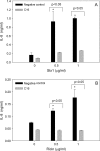
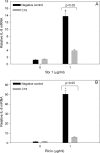
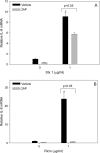
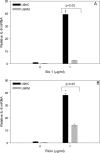
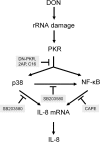
Translational inhibitors such as the trichothecene mycotoxin deoxynivalenol (DON) and ribosomal inhibitory proteins (RIPs) induce mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-driven chemokine and cytokine production by a mechanism known as the ribotoxic stress response (RSR). Double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase (PKR) associates with the ribosome making it uniquely positioned to sense 28S ribosomal RNA damage and initiate the RSR. We have previously shown that PKR mediates DON-induced MAPK phosphorylation in macrophages and monocytes. The purpose of this study was to test the hypothesis that PKR is essential for induction of interleukin (IL)-8 expression in monocytes by DON and two prototypical RIPs, ricin, and Shiga toxin 1 (Stx1). Preincubation of human monocytic U937 cells with the PKR inhibitors C16 and 2-aminopurine (2-AP) blocked DON-induced expression of IL-8 protein and mRNA. Induction of IL-8 expression was similarly impaired in U937 cells stably transfected with a dominant negative PKR plasmid (UK9M) as compared with cells transfected with control plasmid (UK9C). Nuclear factor-kappa B binding, which has been previously shown to be a requisite for DON-induced IL-8 transcription, was markedly reduced in UK9M cells as compared with UK9C cells. As observed for DON, ricin-, and Stx1-induced IL-8 expression was suppressed by the PKR inhibitors C16 and 2-AP as well as impaired in UK9M cells. Taken together, these data indicate that PKR plays a common role in IL-8 induction by DON and the two RIPs, suggesting that this kinase might be a critical factor in RSR.
Figures


References
-
- Alisi A, Spaziani A, Anticoli S, Ghidinelli M, Balsano C. PKR is a novel functional direct player that coordinates skeletal muscle differentiation via p38MAPK/AKT pathways. Cell Signal. 2008;20:534–542. - PubMed
-
- Alzoghaibi MA, Walsh SW, Willey A, Fowler AAB, Graham MF. Linoleic acid, but not oleic acid, upregulates the production of interleukin-8 by human intestinal smooth muscle cells isolated from patients with Crohn's disease. Clin. Nutr. 2003;22:529–535. - PubMed
-
- Andreoli SP. The pathophysiology of the hemolytic uremic syndrome. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 1999;8:459–464. - PubMed
-
- Banks C, Bateman A, Payne R, Johnson P, Sheron N. Chemokine expression in IBD. Mucosal chemokine expression is unselectively increased in both ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. J. Pathol. 2003;199:28–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

