Interdependent roles for hypoxia inducible factor and nuclear factor-kappaB in hypoxic inflammation
- PMID: 18599532
- PMCID: PMC2652186
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.157669
Interdependent roles for hypoxia inducible factor and nuclear factor-kappaB in hypoxic inflammation
Abstract
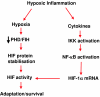
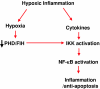
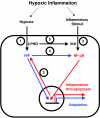
Decreased oxygen availability (hypoxia) is a hallmark feature of the microenvironment in a number of chronic inflammatory conditions including arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Recent advances in our understanding of oxygen-dependent cell signalling have uncovered several mechanisms by which hypoxia impacts upon the development of inflammation through the coordinated expression of adaptive, inflammatory and apoptotic genes. Two central transcription factors involved in the regulation of this response are hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) and nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) which display different degrees of sensitivity to activation during hypoxia. Furthermore, HIF and NF-kappaB demonstrate an intimate interdependence at several mechanistic levels. Recent studies indicate that these pathways may represent important new therapeutic targets in diseases characterized by hypoxic inflammation.
Figures
References
-
- Bernhardt WM, Câmpean V, Kany S, Jürgensen JS, Weidemann A, Warnecke C, Arend M, Klaus S, Günzler V, Amann K, Willam C, Wiesener MS, Eckardt KU. Preconditional activation of hypoxia-inducible factors ameliorates ischemic acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:1970–1978. - PubMed
-
- Bonello S, Zähringer C, BelAiba RS, Djordjevic T, Hess J, Michiels C, Kietzmann T, Görlach A. Reactive oxygen species activate the HIF-1α promoter via a functional NFκB site. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007;27:755–761. - PubMed
-
- Bracken CP, Whitelaw ML, Peet DJ. Activity of hypoxia-inducible factor 2a is regulated by association with the NF-κB essential modulator. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:14240–14251. - PubMed
-
- Chen LW, Egan L, Li ZW, Greten FR, Kagnoff MF, Karin M. The two faces of IKK and NF-κB inhibition: prevention of systemic inflammation but increased local injury following intestinal ischemia-reperfusion. Nat Med. 2003;9:575–581. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

