Human solute carrier SLC6A14 is the beta-alanine carrier
- PMID: 18599538
- PMCID: PMC2592472
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.154500
Human solute carrier SLC6A14 is the beta-alanine carrier
Abstract
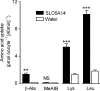
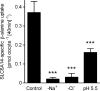
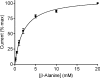
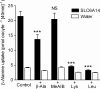
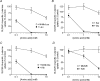
The beta-alanine carrier was characterized functionally in the 1960s to 1980s at the luminal surface of the ileal mucosal wall and is a Na(+)- and Cl(-)-dependent transporter of a number of essential and non-essential cationic and dipolar amino acids including lysine, arginine and leucine. beta-Alanine carrier-like function has not been demonstrated by any solute carrier transport system identified at the molecular level. A series of experiments were designed to determine whether solute carrier SLC6A14 is the molecular correlate of the intestinal beta-alanine carrier, perhaps the last of the classical intestinal amino acid transport systems to be identified at the molecular level. Following expression of the human SLC6A14 transporter in Xenopus laevis oocytes, the key functional characteristics of the beta-alanine carrier, identified previously in situ in ileum, were demonstrated for the first time. The transport system is both Na(+) and Cl(-) dependent, can transport non-alpha-amino acids such as beta-alanine with low affinity, and has a higher affinity for dipolar and cationic amino acids such as leucine and lysine. N-methylation of its substrates reduces the affinity for transport. These observations confirm the hypothesis that the SLC6A14 gene encodes the transport protein known as the beta-alanine carrier which, due to its broad substrate specificity, is likely to play an important role in absorption of essential nutrients and drugs in the distal regions of the human gastrointestinal tract.
Figures

References
-
- Andersen V, Munck BG. Transport of the α-amino-mono-carboxylic acid L-alanine by the β-alanine carrier of the rabbit ileum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987;902:145–148. - PubMed
-
- Anderson CMH, Grenade DS, Boll M, Foltz M, Wake KA, Kennedy DJ, Munck LK, Miyauchi S, Taylor PM, Campbell FC, Munck BG, Daniel H, Ganapathy V, Thwaites DT. H+/amino acid transporter 1 (PAT1) is the imino acid carrier: an intestinal nutrient/drug transporter in human and rat. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:1410–1422. - PubMed
-
- Chen NH, Reith ME, Quick MW. Synaptic uptake and beyond: the sodium- and chloride-dependent neurotransmitter transporter family SLC6. Pflugers Arch. 2004;447:519–531. - PubMed
-
- Durand E, Boutin P, Meyre D, Charles MA, Clement K, Dina C, Froguel P. Polymorphisms in the amino acid transporter solute carrier family 6 (neurotransmitter transporter) member 14 gene contribute to polygenic obesity in French Caucasians. Diabetes. 2004;53:2483–2486. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

