Conditional deletion of the retinoblastoma (Rb) gene in ovarian granulosa cells leads to premature ovarian failure
- PMID: 18599617
- PMCID: PMC2631371
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2008-0033
Conditional deletion of the retinoblastoma (Rb) gene in ovarian granulosa cells leads to premature ovarian failure
Abstract
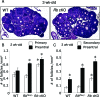
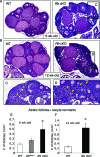
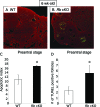
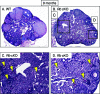
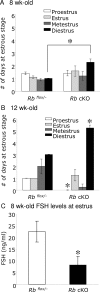
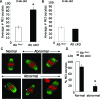
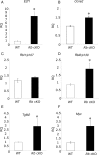
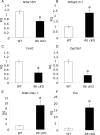
The retinoblastoma protein (RB) regulates cell proliferation and survival by binding to the E2F family of transcription factors. Recent studies suggest that RB also regulates differentiation in a variety of cell types, including myocytes, neurons, adipocytes, and chondrocytes. Rb mutations have been found in ovarian cancer; however, the role of RB in normal and abnormal ovarian function remains unclear. To test the hypothesis that loss of Rb induces ovarian tumorigenesis, we generated an ovarian granulosa cell conditional knockout of Rb (Rb cKO) using the Cre/lox recombination system. Rb cKO females showed 100% survival and no ovarian tumor formation through 9 months of age, but they developed progressive infertility. Prepubertal Rb cKO females showed increased ovulation rates compared with controls, correlating with increased follicle recruitment, higher Fshr and Kitl mRNA levels, and lower anti-Müllerian hormone levels. In contrast, the ovulation rate of 6-wk-old females was similar to that of controls. Morphometric analysis of Rb cKO ovaries from 6-wk-old and older females showed increased follicular atresia and apoptosis. Rb cKO ovaries and preantral follicles had abnormal levels of known direct and indirect target genes of RB, including Rbl2/p130, E2f1, Ccne2, Myc, Fos, and Tgfb2. In addition, preantral follicles showed increased expression of the granulosa cell differentiation marker Inha, decreased levels of Foxl2 and Cyp19a1 aromatase, and abnormal expression of the nuclear receptors Nr5a1, Nr5a2, and Nr0b1. Taken together, our results suggest that RB is required for the temporal-specific pattern of expression of key genes involved in follicular development.
Figures



References
-
- Pestell RG, Albanese C, Reutens AT, Segall JE, Lee RJ, Arnold A 1999 The cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors in hormonal regulation of proliferation and differentiation. Endocr Rev 20:501–534 - PubMed
-
- Classon M, Harlow E 2002 The retinoblastoma tumour suppressor in development and cancer. Nat Rev 2:910–917 - PubMed
-
- Nevins JR 2001 The Rb/E2F pathway and cancer. Hum Mol Genet 10:699–703 - PubMed
-
- Harbour JW, Dean DC 2000 The Rb/E2F pathway: expanding roles and emerging paradigms. Genes Dev 14:2393–2409 - PubMed
-
- Elledge SJ, Winston J, Harper JW 1996 A question of balance: the role of cyclin-kinase inhibitors in development and tumorigenesis. Trends Cell Biol 6:388–392 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

