The IFN-gamma-induced transcriptional program of the CIITA gene is inhibited by statins
- PMID: 18601229
- PMCID: PMC2692880
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.200838189
The IFN-gamma-induced transcriptional program of the CIITA gene is inhibited by statins
Abstract
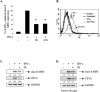
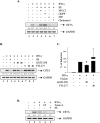
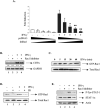
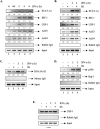
Statins are 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors that exert anti-inflammatory effects. IFN-gamma induction of class II MHC expression, which requires the class II transactivator (CIITA), is inhibited by statins; however, the molecular basis for suppression is undetermined. We describe that statins inhibit IFN-gamma-induced class II MHC expression by suppressing CIITA gene expression, which is dependent on the HMG-CoA reductase pathway. In addition, CIITA expression is inhibited by GGTI-298 or Clostridium difficile Toxin A, specific inhibitors of Rho family protein prenylation, indicating the involvement of small GTPases. Rac1 is involved in IFN-gamma inducible expression of CIITA, and statins inhibit IFN-gamma-induced Rac1 activation, contributing to the inhibitory effect of statins. IFN-gamma induction of the CIITA gene is regulated by the transcription factors STAT-1alpha, interferon regulatory factor (IRF)-1 and upstream stimulatory factor (USF)-1. We previously reported that statins inhibit constitutive STAT-1alpha expression. IRF-1, a STAT-1 dependent gene, is also inhibited by statins. Therefore, statin treatment results in decreased recruitment of STAT-1alpha and IRF-1 to the endogenous CIITA promoter IV (pIV). The recruitment of USF-1 to CIITA pIV is also reduced by statins, as is the recruitment of RNA polymerase II (Pol II), p300 and Brg-1. These data indicate that statins inhibit the transcriptional program of the CIITA gene.
Figures

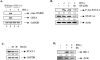
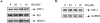

References
-
- Turesson C. Endothelial expression of MHC class II molecules in autoimmune disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004;10:129–143. - PubMed
-
- O'Keefe GM, Nguyen VT, Benveniste EN. Regulation and function of class II major histocompatibility complex, CD40, and B7 expression in macrophages and microglia: Implications in neurological diseases. J. Neurovirol. 2002;8:496–512. - PubMed
-
- Feldmann M, Brennan FM, Maini RN. Rheumatoid arthritis. Cell. 1996;85:307–310. - PubMed
-
- Dyment DA, Sadovnick AD, Ebers GC. Genetics of multiple sclerosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1997;6:1693–1698. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

