A high-resolution radiation hybrid map of rhesus macaque chromosome 5 identifies rearrangements in the genome assembly
- PMID: 18601997
- PMCID: PMC2605074
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2008.05.013
A high-resolution radiation hybrid map of rhesus macaque chromosome 5 identifies rearrangements in the genome assembly
Abstract
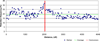
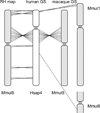
A 10,000-rad radiation hybrid (RH) cell panel of the rhesus macaque was generated to construct a comprehensive RH map of chromosome 5. The map represents 218 markers typed in 185 RH clones. The 4846-cR map has an average marker spacing of 798 kb. Alignments of the RH map to macaque and human genome sequences confirm a large inversion and reveal a previously unreported telomeric inversion. The macaque genome sequence indicates small translocations from the ancestral homolog of macaque chromosome 5 to macaque chromosomes 1 and 6. The RH map suggests that these are probably assembly artifacts. Unlike the genome sequence, the RH mapping data indicate the conservation of synteny between macaque chromosome 5 and human chromosome 4. This study shows that the 10,000-rad panel is appropriate for the generation of a high-resolution whole-genome RH map suitable for the verification of the rhesus genome assembly.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A first generation whole genome RH map of the river buffalo with comparison to domestic cattle.BMC Genomics. 2008 Dec 24;9:631. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-631. BMC Genomics. 2008. PMID: 19108729 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing radiation hybrid mapping through whole genome amplification.Hereditas. 2010 Apr;147(2):103-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.2010.02166.x. Hereditas. 2010. PMID: 20536549 Free PMC article.
-
A high-resolution comparative map of porcine chromosome 4 (SSC4).Anim Genet. 2011 Aug;42(4):440-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2052.2010.02140.x. Epub 2010 Dec 1. Anim Genet. 2011. PMID: 21749428
-
A 12,000-rad porcine radiation hybrid (IMNpRH2) panel refines the conserved synteny between SSC12 and HSA17.Genomics. 2005 Dec;86(6):731-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2005.08.006. Epub 2005 Nov 11. Genomics. 2005. PMID: 16289748
-
A high resolution radiation hybrid map of bovine chromosome 14 identifies scaffold rearrangement in the latest bovine assembly.BMC Genomics. 2007 Jul 26;8:254. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-254. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17655763 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Physical mapping resources for large plant genomes: radiation hybrids for wheat D-genome progenitor Aegilops tauschii.BMC Genomics. 2012 Nov 5;13:597. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-597. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23127207 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Cytogenetic Analysis of One African and Five Asian Macaque Species Reveals Identical Karyotypes as in Mandrill.Curr Genomics. 2018 Apr;19(3):207-215. doi: 10.2174/1389202918666170721115047. Curr Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29606908 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic analysis of genome rearrangements among five mammalian orders.Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2012 Dec;65(3):871-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2012.08.008. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2012. PMID: 22929217 Free PMC article.
-
A new rhesus macaque assembly and annotation for next-generation sequencing analyses.Biol Direct. 2014 Oct 14;9(1):20. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-9-20. Biol Direct. 2014. PMID: 25319552 Free PMC article.
-
DNA repair and crossing over favor similar chromosome regions as discovered in radiation hybrid of Triticum.BMC Genomics. 2012 Jul 24;13:339. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-339. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22827734 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gibbs RA, et al. Evolutionary and biomedical insights from the rhesus macaque genome. Science. 2007;316:222–234. - PubMed
-
- Olivier M, et al. A high-resolution radiation hybrid map of the human genome draft sequence. Science. 2001;291:1298–1302. - PubMed
-
- Weikard R, Goldammer T, Laurent P, Womack JE, Kuehn C. A gene-based high-resolution comparative radiation hybrid map as a framework for genome sequence assembly of a bovine chromosome 6 region associated with QTL for growth, body composition, and milk performance traits. BMC Genomics. 2006;7:53. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

