The extracellular matrix of hydra is a porous sheet and contains type IV collagen
- PMID: 18602803
- PMCID: PMC2560992
- DOI: 10.1016/j.zool.2007.11.004
The extracellular matrix of hydra is a porous sheet and contains type IV collagen
Erratum in
- Zoology (Jena). 2009;112(1):76
Abstract
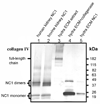
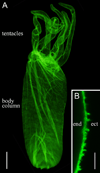
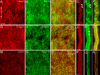
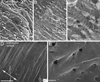
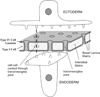
Hydra, as an early diploblastic metazoan, has a well-defined extracellular matrix (ECM) called mesoglea. It is organized in a tri-laminar pattern with one centrally located interstitial matrix that contains type I collagen and two sub-epithelial zones that resemble a basal lamina containing laminin and possibly type IV collagen. This study used monoclonal antibodies to the three hydra mesoglea components (type I, type IV collagens and laminin) and immunofluorescent staining to visualize hydra mesoglea structure and the relationship between these mesoglea components. In addition, hydra mesoglea was isolated free of cells and studied with immunofluorescence and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Our results show that type IV collagen co-localizes with laminin in the basal lamina whereas type I collagen forms a grid pattern of fibers in the interstitial matrix. The isolated mesoglea can maintain its structural stability without epithelial cell attachment. Hydra mesoglea is porous with multiple trans-mesoglea pores ranging from 0.5 to 1 microm in diameter and about six pores per 100 microm(2) in density. We think these trans-mesoglea pores provide a structural base for epithelial cells on both sides to form multiple trans-mesoglea cell-cell contacts. Based on these findings, we propose a new model of hydra mesoglea structure.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cloning and biological function of laminin in Hydra vulgaris.Dev Biol. 1994 Jul;164(1):312-24. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1201. Dev Biol. 1994. PMID: 8026633
-
Extracellular matrix (mesoglea) of Hydra vulgaris III. Formation and function during morphogenesis of hydra cell aggregates.Dev Biol. 1993 Jun;157(2):383-98. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1143. Dev Biol. 1993. PMID: 8500651
-
Extracellular matrix (mesoglea) of Hydra vulgaris. I. Isolation and characterization.Dev Biol. 1991 Dec;148(2):481-94. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90266-6. Dev Biol. 1991. PMID: 1743396
-
Components, structure, biogenesis and function of the Hydra extracellular matrix in regeneration, pattern formation and cell differentiation.Int J Dev Biol. 2012;56(6-8):567-76. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.113445ms. Int J Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22689358 Review.
-
Extracellular matrix and morphogenesis in cnidarians: a tightly knit relationship.Essays Biochem. 2019 Sep 13;63(3):407-416. doi: 10.1042/EBC20190021. Print 2019 Sep 13. Essays Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31462530 Review.
Cited by
-
Bud detachment in hydra requires activation of fibroblast growth factor receptor and a Rho-ROCK-myosin II signaling pathway to ensure formation of a basal constriction.Dev Dyn. 2017 Jul;246(7):502-516. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.24508. Epub 2017 May 22. Dev Dyn. 2017. PMID: 28411398 Free PMC article.
-
Micro- and macrorheology of jellyfish extracellular matrix.Biophys J. 2012 Jan 4;102(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.11.4004. Epub 2012 Jan 3. Biophys J. 2012. PMID: 22225792 Free PMC article.
-
A unique covalent bond in basement membrane is a primordial innovation for tissue evolution.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jan 7;111(1):331-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1318499111. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24344311 Free PMC article.
-
Maintenance of a Protein Structure in the Dynamic Evolution of TIMPs over 600 Million Years.Genome Biol Evol. 2016 Apr 13;8(4):1056-71. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evw052. Genome Biol Evol. 2016. PMID: 26957029 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo imaging of basement membrane movement: ECM patterning shapes Hydra polyps.J Cell Sci. 2011 Dec 1;124(Pt 23):4027-38. doi: 10.1242/jcs.087239. J Cell Sci. 2011. PMID: 22194305 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borza DB, Bondar O, Colon S, Todd P, Sado Y, Neilson EG, Hudson BG. Goodpasture autoantibodies unmask cryptic epitopes by selectively dissociating autoantigen complexes lacking structural reinforcement. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:27147–27154. - PubMed
-
- Day RM, Lenhoff HM. Hydra mesoglea: a model for investigating epithelial cell-basement membrane interactions. Science. 1981;211:291–294. - PubMed
-
- Day RM, Lenhoff HM. Isolating mesolamellae. In: Lenhoff HM, editor. Hydra: Research Methods. New York: Plenum Press; 1983. pp. 327–329.
-
- Deutzmann R, Fowler S, Zhang X, Boone K, Dexter S, Boot-Handford RP, Rachel R, Sarras MP. Molecular, biochemical and functional analysis of a novel and developmentally important fibrillar collagen (Hcol-I) in hydra. Development. 2000;127:4669–4680. - PubMed
-
- Epp L, Smid I, Tardent P. Synthesis of the mesoglea by ectoderm and endoderm in reassembled hydra. J. Morphol. 1986;189:271–279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

