Endocytosis of apolipoprotein A-V by members of the low density lipoprotein receptor and the VPS10p domain receptor families
- PMID: 18603531
- PMCID: PMC2533778
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M802721200
Endocytosis of apolipoprotein A-V by members of the low density lipoprotein receptor and the VPS10p domain receptor families
Abstract
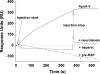
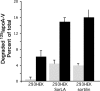
Apolipoprotein A-V (apoA-V) is present in low amounts in plasma and has been found to modulate triacylglycerol levels in humans and in animal models. ApoA-V displays affinity for members of the low density lipoprotein receptor (LDL-R) gene family, known as the classical lipoprotein receptors, including LRP1 and SorLA/LR11. In addition to LDL-A binding repeats, the mosaic receptor SorLA/LR11 also possesses a Vps10p domain. Here we show that apoA-V also binds to sortilin, a receptor from the Vsp10p domain gene family that lacks LDL-A repeats. Binding of apoA-V to sortilin was competed by neurotensin, a ligand that binds specifically to the Vps10p domain. To investigate the biological fate of receptor-bound apoA-V, binding experiments were conducted with cultured human embryonic kidney cells transfected with either SorLA/LR11 or sortilin. Compared with nontransfected cells, apoA-V binding to SorLA/LR11- and sortilin-expressing cells was markedly enhanced. Internalization experiments, live imaging studies, and fluorescence resonance energy transfer analyses demonstrated that labeled apoA-V was rapidly internalized, co-localized with receptors in early endosomes, and followed the receptors through endosomes to the trans-Golgi network. The observed decrease of fluorescence signal intensity as a function of time during live imaging experiments suggested ligand uncoupling in endosomes with subsequent delivery to lysosomes for degradation. This interpretation was supported by experiments with (125)I-labeled apoA-V, demonstrating clear differences in degradation between transfected and nontransfected cells. We conclude that apoA-V binds to receptors possessing LDL-A repeats and Vsp10p domains and that apoA-V is internalized into cells via these receptors. This could be a mechanism by which apoA-V modulates lipoprotein metabolism in vivo.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The mosaic receptor sorLA/LR11 binds components of the plasminogen-activating system and platelet-derived growth factor-BB similarly to LRP1 (low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein), but mediates slow internalization of bound ligand.Biochem J. 2004 Jul 1;381(Pt 1):203-12. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040149. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 15053742 Free PMC article.
-
Activation and functional characterization of the mosaic receptor SorLA/LR11.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jun 22;276(25):22788-96. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M100857200. Epub 2001 Apr 9. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11294867
-
Apolipoprotein A-V interaction with members of the low density lipoprotein receptor gene family.Biochemistry. 2007 Mar 27;46(12):3896-904. doi: 10.1021/bi7000533. Epub 2007 Feb 28. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17326667
-
The Vps10p-domain receptor family.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009 Aug;66(16):2677-89. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0043-1. Epub 2009 May 12. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19434368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low-density lipoprotein receptor family: endocytosis and signal transduction.Mol Neurobiol. 2001 Feb;23(1):53-67. doi: 10.1385/MN:23:1:53. Mol Neurobiol. 2001. PMID: 11642543 Review.
Cited by
-
A new role under sortilin's belt in cancer.Commun Integr Biol. 2016 Jan 11;9(1):e1130192. doi: 10.1080/19420889.2015.1130192. eCollection 2016 Jan-Feb. Commun Integr Biol. 2016. PMID: 27066187 Free PMC article.
-
Sorting protein-related receptor SorLA controls regulated secretion of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 2;286(48):41871-41882. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.246413. Epub 2011 Oct 12. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21994944 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid-Forming Properties of Human Apolipoproteins: Sequence Analyses and Structural Insights.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;855:175-211. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-17344-3_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26149931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sortilin, encoded by the cardiovascular risk gene SORT1, and its suggested functions in cardiovascular disease.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2015 Apr;17(4):496. doi: 10.1007/s11883-015-0496-7. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2015. PMID: 25702058 Review.
-
Activation of ER stress and mTORC1 suppresses hepatic sortilin-1 levels in obese mice.J Clin Invest. 2012 May;122(5):1677-87. doi: 10.1172/JCI61248. Epub 2012 Apr 2. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 22466652 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pennacchio, L. A., Olivier, M., Hubacek, J. A., Cohen, J. C., Cox, D. R., Fruchart, J. C., Krauss, R. M., and Rubin, E. M. (2001) Science 294169 –173 - PubMed
-
- van Dijk, K. W., Rensen, P.C., Voshol, P. J., and Havekes, L. M. (2004) Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 15239 –246 - PubMed
-
- Hubacek, J. A. (2005) Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 43897 –902 - PubMed
-
- Talmud, P. J., Hawe, E., Martin, S., Olivier, M., Miller, G. J., Rubin, E. M., Pennacchio, L. A., and Humphries, S. E. (2002) Hum. Mol. Genet. 113039 –3046 - PubMed
-
- Yamada, Y., Kato, K., Hibino, T., Yokoi, K., Matsuo, H., Segawa, T., Watanabe, S., Ichihara, S., Yoshida, H., Satoh, K., and Nozawa, Y. (2007) Atherosclerosis 191298 –304 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

