Interaction with the hERG channel and cytotoxicity of amiodarone and amiodarone analogues
- PMID: 18604229
- PMCID: PMC2579668
- DOI: 10.1038/bjp.2008.287
Interaction with the hERG channel and cytotoxicity of amiodarone and amiodarone analogues
Abstract
Background and purpose: Amiodarone (2-n-butyl-3-[3,5 diiodo-4-diethylaminoethoxybenzoyl]-benzofuran, B2-O-CH(2)CH(2)-N-diethyl) is an effective class III antiarrhythmic drug demonstrating potentially life-threatening organ toxicity. The principal aim of the study was to find amiodarone analogues that retained human ether-a-go-go-related protein (hERG) channel inhibition but with reduced cytotoxicity.
Experimental approach: We synthesized amiodarone analogues with or without a positively ionizable nitrogen in the phenolic side chain. The cytotoxic properties of the compounds were evaluated using HepG2 (a hepatocyte cell line) and A549 cells (a pneumocyte line). Interactions of all compounds with the hERG channel were measured using pharmacological and in silico methods.
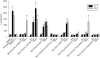
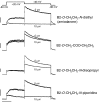
Key results: Compared with amiodarone, which displayed only a weak cytotoxicity, the mono- and bis-desethylated metabolites, the further degraded alcohol (B2-O-CH(2)-CH(2)-OH), the corresponding acid (B2-O-CH(2)-COOH) and, finally, the newly synthesized B2-O-CH(2)-CH(2)-N-pyrrolidine were equally or more toxic. Conversely, structural analogues such as the B2-O-CH(2)-CH(2)-N-diisopropyl and the B2-O-CH(2)-CH(2)-N-piperidine were significantly less toxic than amiodarone. Cytotoxicity was associated with a drop in the mitochondrial membrane potential, suggesting mitochondrial involvement. Pharmacological and in silico investigations concerning the interactions of these compounds with the hERG channel revealed that compounds carrying a basic nitrogen in the side chain display a much higher affinity than those lacking such a group. Specifically, B2-O-CH(2)-CH(2)-N-piperidine and B2-O-CH(2)-CH(2)-N-pyrrolidine revealed a higher affinity towards hERG channels than amiodarone.
Conclusions and implications: Amiodarone analogues with better hERG channel inhibition and cytotoxicity profiles than the parent compound have been identified, demonstrating that cytotoxicity and hERG channel interaction are mechanistically distinct and separable properties of the compounds.
Figures
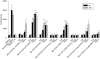
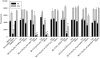
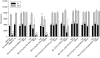

Similar articles
-
Hepatocellular toxicity and pharmacological effect of amiodarone and amiodarone derivatives.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Dec;319(3):1413-23. doi: 10.1124/jpet.106.108993. Epub 2006 Sep 13. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006. PMID: 16971508
-
Characterization of recombinant hERG K(+) channel inhibition by the active metabolite of amiodarone desethyl-amiodarone.J Electrocardiol. 2010 Sep-Oct;43(5):440-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2010.04.007. Epub 2010 May 20. J Electrocardiol. 2010. PMID: 20493497
-
High affinity HERG K(+) channel blockade by the antiarrhythmic agent dronedarone: resistance to mutations of the S6 residues Y652 and F656.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Dec 17;325(3):883-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.10.127. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. PMID: 15541373
-
The cardiac hERG/IKr potassium channel as pharmacological target: structure, function, regulation, and clinical applications.Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12(18):2271-83. doi: 10.2174/138161206777585102. Curr Pharm Des. 2006. PMID: 16787254 Review.
-
Relationship among amiodarone, new class III antiarrhythmics, miscellaneous agents and acquired long QT syndrome.Cardiol J. 2008;15(3):209-19. Cardiol J. 2008. PMID: 18651412 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural modeling of hERG channel-drug interactions using Rosetta.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Nov 14;14:1244166. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1244166. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38035013 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the K+ conductance and Cole-Moore shift of the oncogenic Kv10.1 channel by amiodarone.Pflugers Arch. 2018 Mar;470(3):491-503. doi: 10.1007/s00424-017-2092-x. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Pflugers Arch. 2018. PMID: 29218452
-
Marine algal toxin azaspiracid is an open-state blocker of hERG potassium channels.Chem Res Toxicol. 2012 Sep 17;25(9):1975-84. doi: 10.1021/tx300283t. Epub 2012 Aug 10. Chem Res Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22856456 Free PMC article.
-
hERG channel function: beyond long QT.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013 Mar;34(3):329-35. doi: 10.1038/aps.2013.6. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013. PMID: 23459091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An antedrug of the CXCL12 neutraligand blocks experimental allergic asthma without systemic effect in mice.J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 26;288(17):11865-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.449348. Epub 2013 Feb 28. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23449983 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bigler L, Spirli C, Fiorotto R, Pettenazzo A, Duner E, Baritussio A, et al. Synthesis and cytotoxicity properties of amiodarone analogues. Eur J Med Chem. 2007;42:861–867. - PubMed
-
- Bolt MW, Card JW, Racz WJ, Brien JF, Massey TE. Disruption of mitochondrial function and cellular ATP levels by amiodarone and N-desethylamiodarone in initiation of amiodarone-induced pulmonary cytotoxicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001a;298:1280–1289. - PubMed
-
- Bolt MW, Racz WJ, Brien JF, Massey TE. Effects of vitamin E on cytotoxicity of amiodarone and N-desethylamiodarone in isolated hamster lung cells. Toxicology. 2001b;166:109–118. - PubMed
-
- Braumann T. Determination of hydrophobic parameters by reversed-phase liquid chromatography: theory, experimental techniques, and application in studies on quantitative structure–activity relationships. J Chromatogr. 1986a;373:191–225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

