Unfolded protein response genes regulated by CED-1 are required for Caenorhabditis elegans innate immunity
- PMID: 18606143
- PMCID: PMC2517226
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.05.006
Unfolded protein response genes regulated by CED-1 are required for Caenorhabditis elegans innate immunity
Abstract
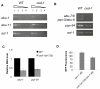
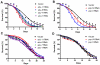
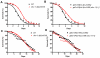
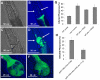
The endoplasmic reticulum stress response, also known as the unfolded protein response (UPR), has been implicated in the normal physiology of immune defense and in several disorders, including diabetes, cancer, and neurodegenerative disease. Here, we show that the apoptotic receptor CED-1 and a network of PQN/ABU proteins involved in a noncanonical UPR response are required for proper defense to pathogen infection in Caenorhabditis elegans. A full-genome microarray analysis indicates that CED-1 functions to activate the expression of pqn/abu genes. We also show that ced-1 and pqn/abu genes are required for the survival of C. elegans exposed to live Salmonella enterica, and that overexpression of pqn/abu genes confers protection against pathogen-mediated killing. The results indicate that unfolded protein response genes, regulated in a CED-1-dependent manner, are involved in the C. elegans immune response to live bacteria.
Figures

Comment in
-
Dangerous liaisons: the apoptotic engulfment receptor CED-1 links innate immunity to the unfolded protein response.Dev Cell. 2008 Jul;15(1):3-4. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.06.007. Dev Cell. 2008. PMID: 18606133 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aballay A, Drenkard E, Hilbun LR, Ausubel FM. Caenorhabditis elegans innate immune response triggered by Salmonella enterica requires intact LPS and is mediated by a MAPK signaling pathway. Curr Biol. 2003;13:47–52. - PubMed
-
- Aballay A, Yorgey P, Ausubel FM. Salmonella typhimurium proliferates and establishes a persistent infection in the intestine of Caenorhabditis elegans. Curr Biol. 2000;10:1539–1542. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

