Different effects of selective dopamine uptake inhibitors, GBR 12909 and WIN 35428, on HIV-1 Tat toxicity in rat fetal midbrain neurons
- PMID: 18606182
- PMCID: PMC4205582
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuro.2008.06.003
Different effects of selective dopamine uptake inhibitors, GBR 12909 and WIN 35428, on HIV-1 Tat toxicity in rat fetal midbrain neurons
Abstract
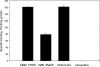
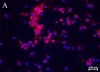
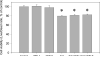
Drug abuse is a risk factor for neurological complications in HIV infection. Cocaine has been shown to exacerbate HIV-associated brain pathology and enhance neurotoxicity of HIV-1 Tat and gp120 proteins. In this study, we found that the selective inhibitor of dopamine transporter (DAT) function, 1-[2-[bis(4-fluorophenyl) methoxy]ethyl]-4-(3-phenylpropyl) piperazine (GBR 12909, vanoxerine), but not the selective inhibitors of serotonin and norepinephrine (SERT and NET) transporters, sertraline and nizoxetine, emulated cocaine-mediated enhancement of Tat neurotoxicity in rat fetal midbrain primary cell cultures. Similar to cocaine, the significant increase of Tat toxicity in midbrain cell cultures was observed at micromolar dose (5microM) of GBR 12909. However, different doses of another selective dopamine uptake inhibitor, WIN 35428 did not affect Tat neurotoxicity. The study supports the hypothesis that changes in control of dopamine (DA) homeostasis are important for the cocaine-mediated enhancement of HIV-1 Tat neurotoxicity. Our results also demonstrate that inhibitors of DA uptake, which can bind to different domains of DAT, differ in their ability to mimic synergistic toxicity of cocaine and HIV-1 Tat in the midbrain cell culture.
Figures


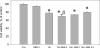
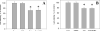
References
-
- Aksenov MY, Hasselrot U, Wu G, Nath A, Anderson C, Mactutus CF, Booze RM. Temporal relationships between HIV-1 Tat-induced neuronal degeneration, OX-42 immunoreactivity, reactive astrocytosis, and protein oxidation in the rat striatum. Brain Res. 2003;987:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Aksenov MY, Aksenova MV, Nath A, Ray PD, Mactutus CF, Booze RM. Cocaine-mediated enhancement of Tat toxicity in rat hippocampal cell cultures: the role of oxidative stress and D1 dopamine receptor. Neurotox. 2006;27:217–228. - PubMed
-
- Aksenova MV, Silvers JM, Aksenov MY, Nath A, Ray PD, Mactutus CF, Booze RM. HIV-1 Tat neurotoxicity in primary cultures of rat midbrain fetal neurons: changes in dopamine transporter binding and immunoreactivity. Neurosci Lett. 2006;395:235–239. - PubMed
-
- Blakely RD, De Felice LJ, Hartzell HC. Molecular physiology of norepinephrine and serotonin transporters. J. Exp. Biol. 1994;196:263–281. - PubMed
-
- Boos TL, Greiner E, Calhoun WJ, Prisinzano TE, Nightingale B, Dersch CM, Rothman RB, Jacobson AE, Rice KC. Structure–activity relationships of substituted N-benzyl piperidines in the GBR series: Synthesis of 4-(2-(bis(4-fluorophenyl) methoxy)ethyl)-1-(2-trifluoromethylbenzyl) piperidine, an allosteric modulator of the serotonin transporter. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 2006;14:3967–3973. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

